Electron transport and mechanism of ATP formation : The synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi in presence of light within the chloroplast is called photophosphorylation. It is of two types - viz., non-cyclic photophosphorylation and cyclic photophosphorylation.
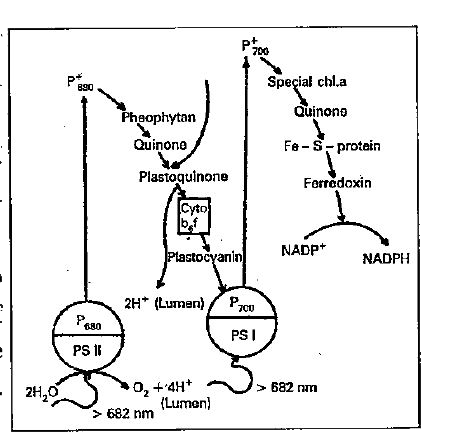
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation : In chloroplasts, the electrons continuously supplied from water, are transported to photosystem-II, to photosystme-I and finally to `NADP^(+)` which is reduced to NADPH. This transport of electrons is called non-cyclic electron transport. Formation of ATP in association with non-cyclic electron transport is called non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Non-cyclic electron transport requires two large, multimolecular complexes called as photosystem - I and photosystem - II. The two complexes operate in series and are linked by electron carrier molecules. The photo systems and electron carriers are arranged in the thylacoid membranes of chloroplasts.
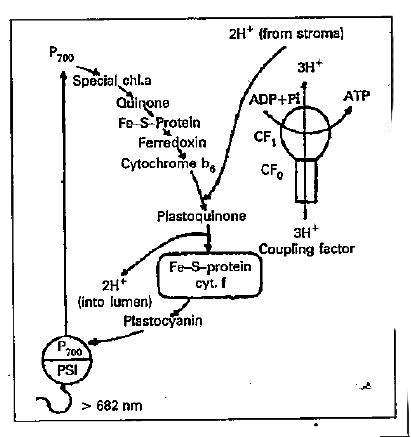
Photosystem-I consists of several molecules of chlorophyll a, some molecules of chlorophyll b and some `beta`-carotene molecules. The reaction centre of PS-I consists of four to six molecules of chlorophyll a and is designated as `P_(700)`. Light harvesting complex I (chlorophyll-protein complexes) is associated with PS I. PS I is activated by red light of longer wavelength (`gt` 682 nm) when PS I absorbs red light, the absorbed light energy is transferred to `P_(700)`. It is first excited and then oxidized. The electron released from `P_(700)` is transferred to a special chlorophyll a. The electron is then passed through quinone and Fe-S-proteins and finally to ferredoxin. From ferredoxin, electron is transferred to `NADP^(+)` which is reduced to NADPH. This reduction takes place in the stroma and catalysed by the enzyme ferredoxin `NADP^(+)` oxidoreductase.
Photosystem-II consists of several molecules o chlorophyll a, some molecules of chlorophyll b and some `beta`-carotene molecules. The reaction centre of PS-II consists of four to six molecules of chlorophyll a and is designated as `P_(680)`. Light harvesting complex-II is associated with PS-II. PS-II is activated by red light of shorter wavelength (`lt` 682 nm). When PS-II absorbs red light, the absorbed light energy is transferred to `P_(680)`. It is first excited and then oxidised. The electron released from `P_(680)` is transferred to pheophytin (a colourless chl. a molecule which lacks magnesium ion). From pheophytin electron is quickly transferred to quinone and then to plastoquinone, which requires two electron. Reduced plastoquinone picks up two protons from stroma and moves from PS-II to cytochrome `b_(6)` f complex. Electrons from reduced plastoquinone are transferred first to Fe-S-protein and then to cytochrome f. Protons released from oxidised plastoquinone diffuse into lumen of thylacoid membrane. From cyt. f the electron is transported to plastocyanin (a mobile protein containing copper ion). From plastocyanin electron moves to `P_(700)` of PS-I, bringing it to reduced or normal state.
The electrons that reduce oxidised `P_(680)` are supplied by a cluster of four manganese ions which are associated with oxygen evolving Complex (OEC) proteins. OEC splits water and releases electrons and oxygen. OEC is located on the lumen side of thylacoid membrane. `Cl^(-)` also bind to OEC.
The result of electron transport from water to PS-II and from PS-II to PS-I is accumulation of protons in the lumen of thylacoid membrane. The thylacoid membrane is impermeable to protons. Thylacoid membrane shows many proton channels called ATP synthase or coupling factors. A coupling factor consists of a basal, hydrophobic complex `(CF_(0))` and apical, hydrophilic complex `(CF_(1)). CF_(1)` contains the active site for ATP synthesis and `CF_(0)` forms a proton channel across the membrane. When protons diffuse from thylacoid lumen into stroma through coupling factor, ATP is synthesised from ADP and Pi.
Cyclic photophosphorylation : In chloroplasts, when sufficient amount of `NADP^(+)` is not available the electrons released from activated `P_(700)` of PS-I return to `P_(700)` through plastoquinone, cytochrome complex and plastocyanin. This electron transport is independent of PS-II and called cyclic electron transport. Formation of ATP associated with cyclic electron transport is called cyclic photophosphorylation.