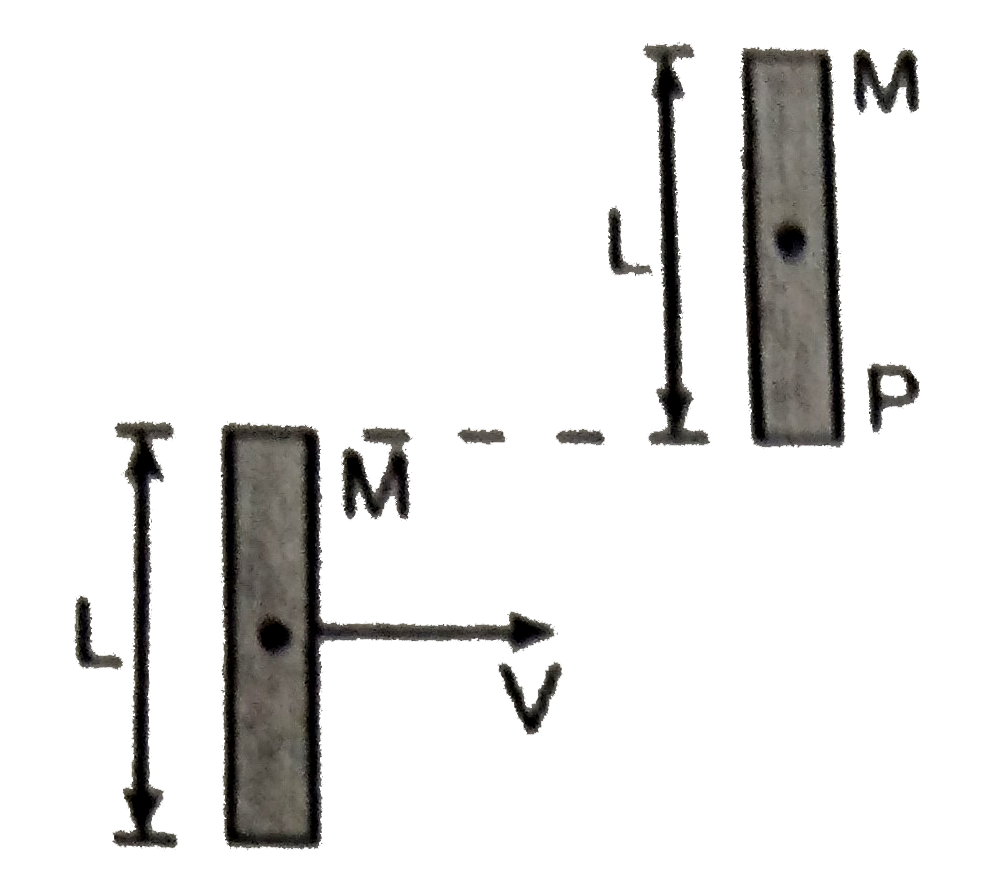
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 66|4 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 67|2 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 64|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|53 VideosELASTICITY AND VISCOCITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Advanced Level Problems|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEMS-DPP 65
- A bar of mass M and length L is in pure traslatory motion with its of ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth tube of certain mass is rotated in a gravity-free Space and r...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R is released from the shown posi...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is //are true.
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder A, of mass 12 kg is being pulled by another weight B(...
Text Solution
|