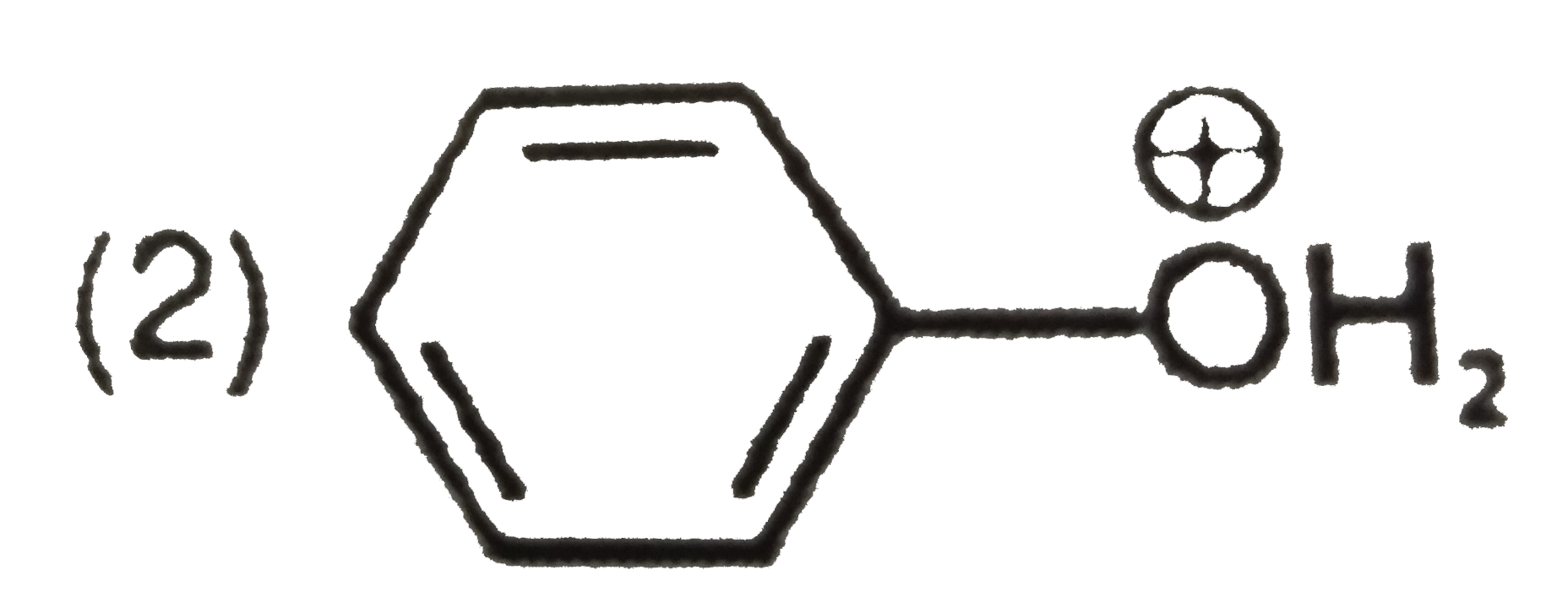
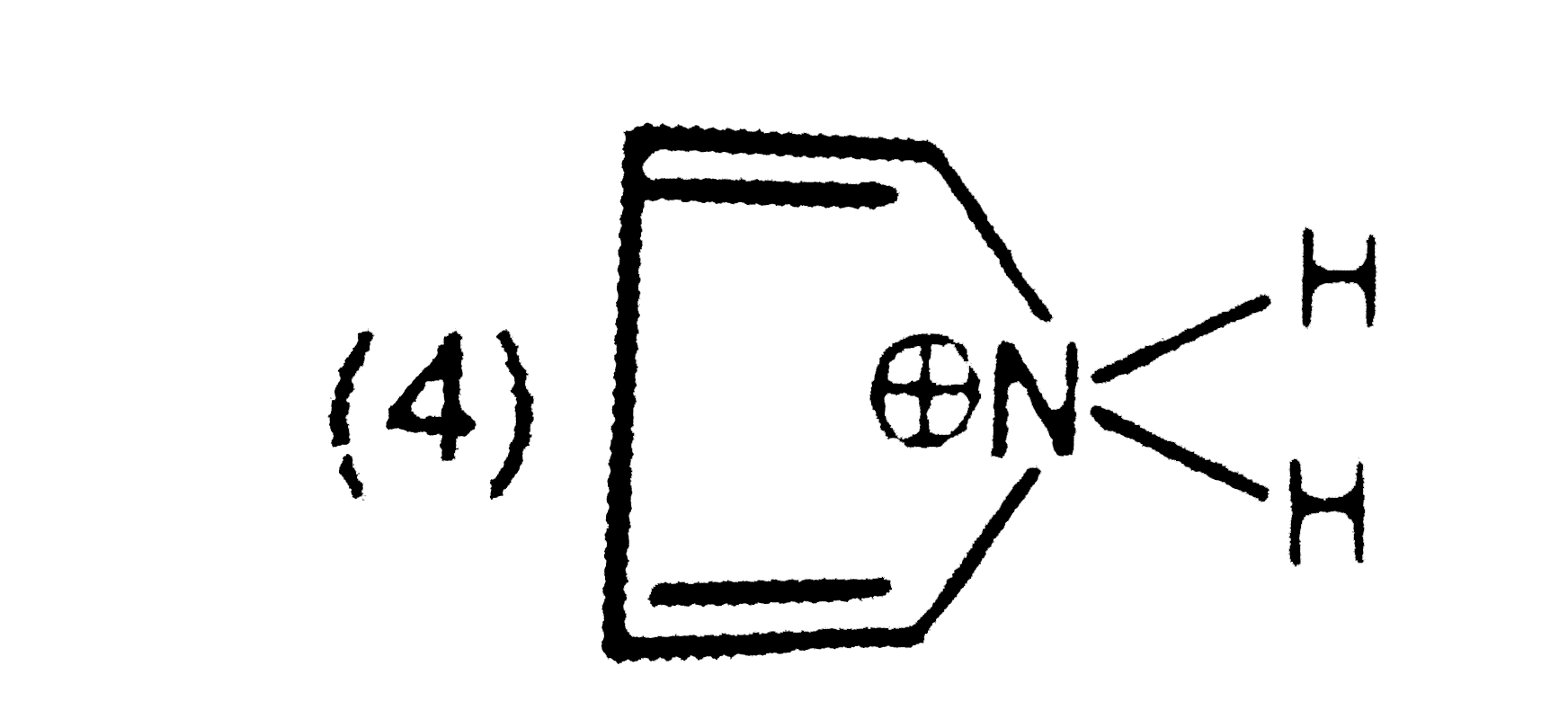A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-2(NSEC)|24 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-III : PRACTICE TEST-2|1 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise JEE(MAIN) ONLINE PROBLEMS|2 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-III: Section-5: Matching List Type|1 VideosHYDROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise INORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrogen & its compunds Y environment chemistry)|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I-PRACTICE TEST-1
- Which of the following compounds is not aromatic ?
Text Solution
|
- Which compound has least e^(-) density in benzene ring
Text Solution
|
- The order of heat of hydrogenation in following compounds is:
Text Solution
|
- Resonance stabilized cation is:
Text Solution
|
- In HCOO^(-) , the two carbon- oxygen bonds to be of equal length. What...
Text Solution
|
- Compare C-N bond length in the following :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is false for order of -l effect :
Text Solution
|
- underset("x")(H-N=C=O)harrunderset("y")(H-overset(o+)N-=C-overset(Thet...
Text Solution
|
- would be :
Text Solution
|
- Number of delocalized e^(-) pairs in squaric acid and dianion of squar...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following benzene ring has greater electron density than ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has the miximum number of resonating structure ...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following the aromatic compound is
Text Solution
|
- overset(Theta)overset(..)CH(2)-underset(O)underset(||)C-CH(3) and CH(2...
Text Solution
|
- Which is not stable
Text Solution
|
- Correct order of stability of following alkenes is
Text Solution
|
- All the carbon-carbon bond lengths are equal in
Text Solution
|
- The kind of delocalisation involving sigma bond orbitals is called……
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has the highest dipole moment.
Text Solution
|
- in C(1)-H, C(2)-H and C(3)-H the homolytic bond dissociation energy or...
Text Solution
|