Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise|8 VideosCO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|8 VideosCO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|8 VideosCIRCLE
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise (long Answer Questions )|5 VideosCONSTRUCTIONS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE|36 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH-CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY -Problems From NCERT/ Exemplar
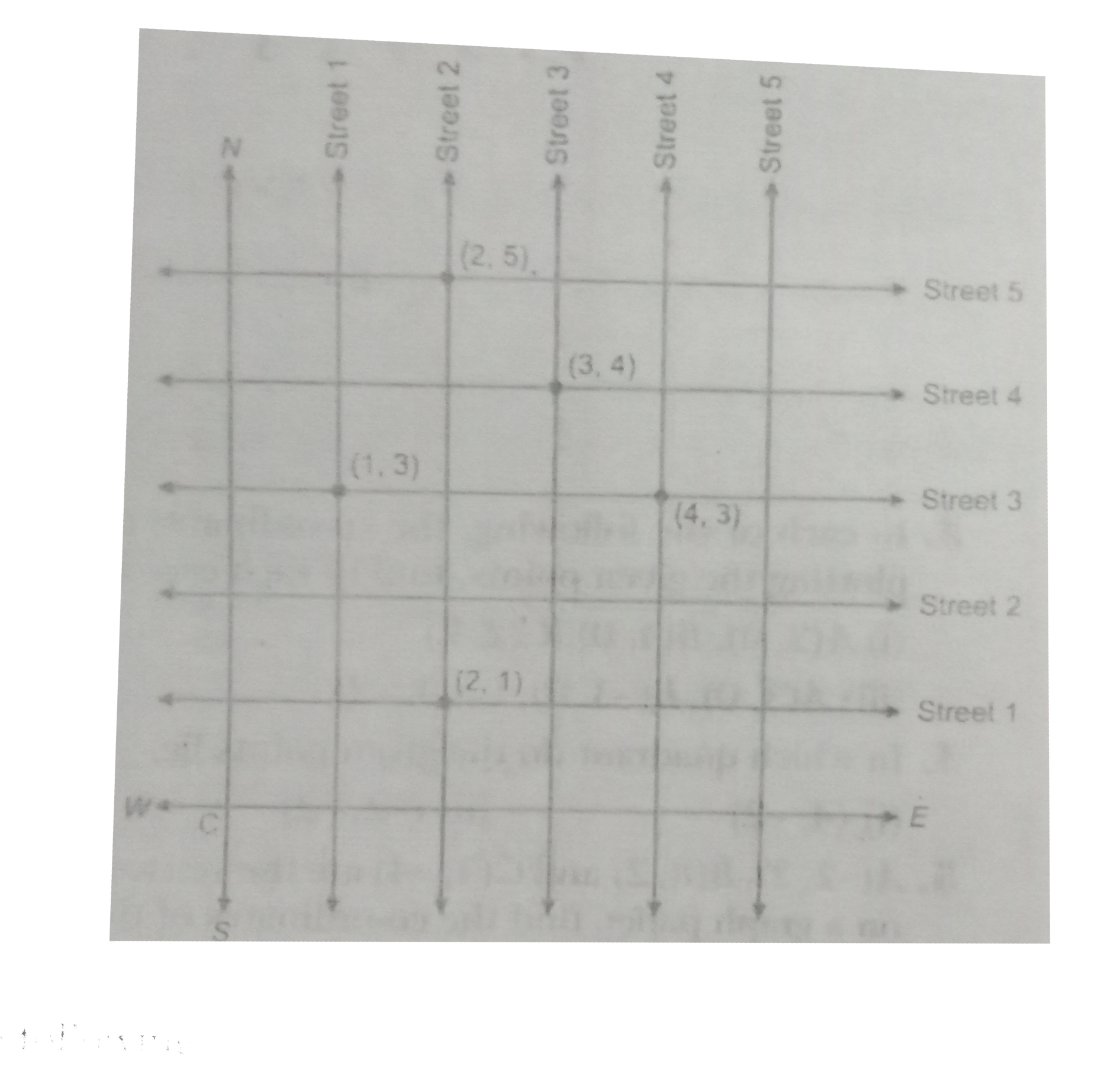
- (Street Plan): A city has two main roads which cross each other at ...
Text Solution
|
- Plot the points (x,y) given in the following table on the plane, choos...
Text Solution
|
- Plot the following points and write the name of the figure obtained by...
Text Solution
|
- Points A(5,3), B(-2,3) and D(5,-4) are three vertices of a square ABCD...
Text Solution
|
- Write the coordinates of the vertices of a rectangle whose length and ...
Text Solution
|
- Plot the points P(1,0), Q(4,0) and S(1,3). Find the coordinates of the...
Text Solution
|