Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by t...
Text Solution
|
- The hydrolyiss of methyl acetate in aqueous solution is has been studi...
Text Solution
|
- For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by t...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by t...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by t...
Text Solution
|
- For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution has been studied by t...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrolysis of ethyl acetate in acidic solution is a pseudo first order...
Text Solution
|
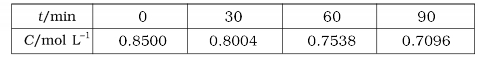 Show that it follows a pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains nearly constant (55 mol L^(-1)), during the course of the reaction. What is the value of k in this equation? Rate = k` [CH_3C00CH_3][H_20]
Show that it follows a pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains nearly constant (55 mol L^(-1)), during the course of the reaction. What is the value of k in this equation? Rate = k` [CH_3C00CH_3][H_20]