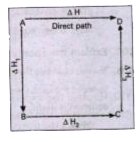
Ness.s Law Hess.s law states that the total amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction is always same whether the reaction is camed out in one step (or) in several steps
illustration : This means that the heat of reaction depends only on the initial and final stages and not on the intermediate stages through which the reaction is carried out. Let us consider a reaction in which A gives D. The reaction is brought out in one step and let the heat of reaction be `triangleH.`
`A to D, triangleH`
Suppose the same reaction is brought out in three stages as follows-
`A to B, triangleH_(1)`
`B to C, triangleH_(2)`
`C to D , triangleH_(3)`
The net heat of reaction is `triangleH_(1)+triangleH_(2)+triangleH_(3)`
According to Hess law `triangleH=triangleH_(1)+triangleH_(2)+triangleH_(3)`.
Ex: Consider the formation of Coz. It can be prepared in two ways.
1) Direct method : By heating carbon in excess of `O_2`
2) Indirect method : Carbon can be converted into `CO_2`, in the following two steps.
`C(s)+1/2 O_(2) (g) to CO_(2) (g) , triangleH_(1)=-110.5kJ`
`CO(g)+1/2 O_(2) (g) to CO_(2) (g), triangleH_(2)=-283.02kJ`
Total `triangleH=-393.52kJ`
Total two `triangleH` values are same.
