Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRICITY
VK GLOBAL PUBLICATION|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTION-I|8 VideosELECTRICITY
VK GLOBAL PUBLICATION|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTION-II|8 VideosELECTRICITY
VK GLOBAL PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT EXERCISE|21 VideosLIGHT-REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
VK GLOBAL PUBLICATION|Exercise PROFICIENCY EXERCISE (Long Answer Questions)|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VK GLOBAL PUBLICATION-ELECTRICITY-VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTION
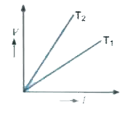
- The voltage-current (V-I) graph of a metallic conductor at two differe...
Text Solution
|
- Why is resistance less when resistors are joined in parallel?
Text Solution
|
- Why is resistance more in series combination?
Text Solution
|
- What are the special features of a heating wire?
Text Solution
|
- What is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter?
Text Solution
|
- Which one has more resistance 100 watt bulb or 60 watt bulb both opera...
Text Solution
|
- Write the expression for the heat energy produced in a wire of resista...
Text Solution
|
- Name the physical quantity whose unit is J//C.
Text Solution
|
- What the resistance of an air gap?
Text Solution
|
- What is the commercial unit of electric energy?
Text Solution
|
- What happens to the resistance of a wire if it is made thinner?
Text Solution
|
- In series combination which remains constant-current or voltage?
Text Solution
|
- Which substance is used for making resistance coil of electric heater ...
Text Solution
|
- Which physical quantity remains constant when resistances are connecte...
Text Solution
|
- How is the ammeter connected in the circuit?
Text Solution
|
- Why is an ammeter connected in series in an electric circuit?
Text Solution
|
- Name two devices in which electricity is converted into heat.
Text Solution
|
- Name the alloy which is used for making the filament of bulbs.
Text Solution
|
- Name the instrument used for measuring potential difference.
Text Solution
|
- Name the instrument used for measuring electric current flowing in an ...
Text Solution
|