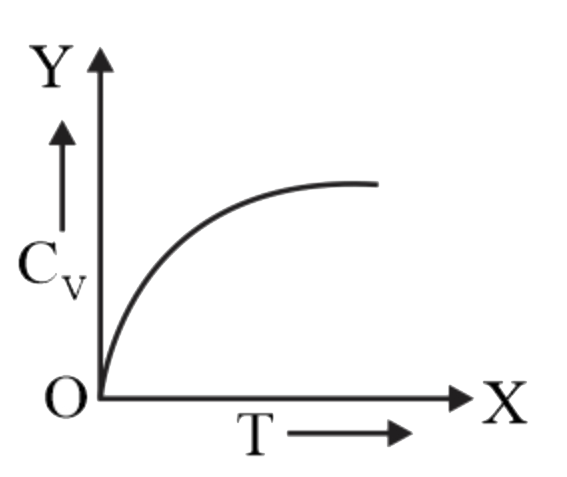
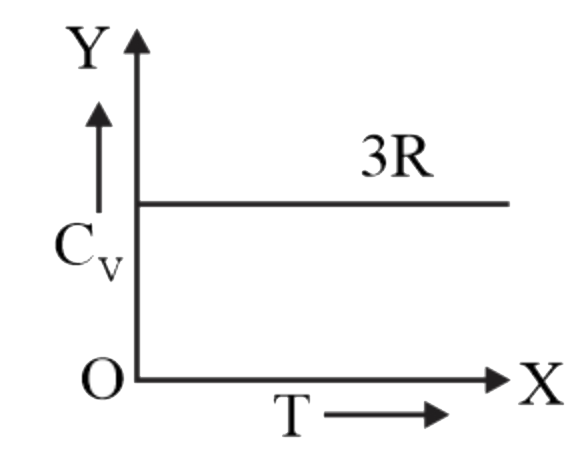
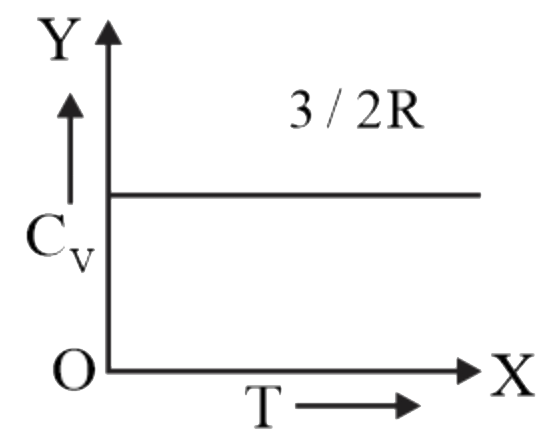
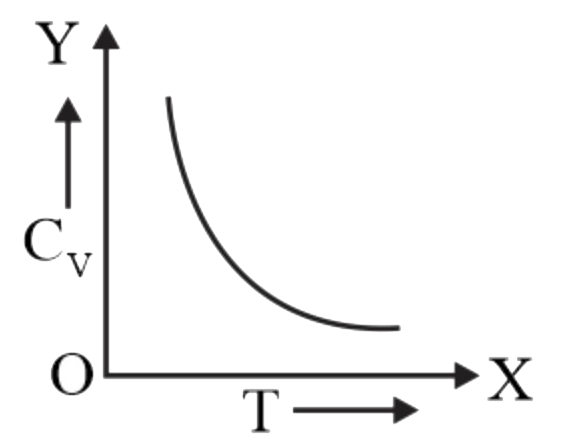
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Graph for specific heat at constant volume for a monoatomic gas
Text Solution
|
- Graph for specific heat at constant volume for a monoatomic gas
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the molar specific heat of monoatomic gas at constant volume...
Text Solution
|
- Graph for specific heat at constant volume for a monoatomic gas
Text Solution
|
- The molar specific heat at constant pressure of monoatomic gas is
Text Solution
|
- One mole of monoatomic gas is mixed with one mole of a diatomic ideal ...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to that at constan...
Text Solution
|
- Graph of specific heat at constant volume for a monoatomic gas is
Text Solution
|
- Molar specific heat at constant volume is C for a monoatomic gas is
Text Solution
|