Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-PROBABILITY I -JEE Advanced Previous Year
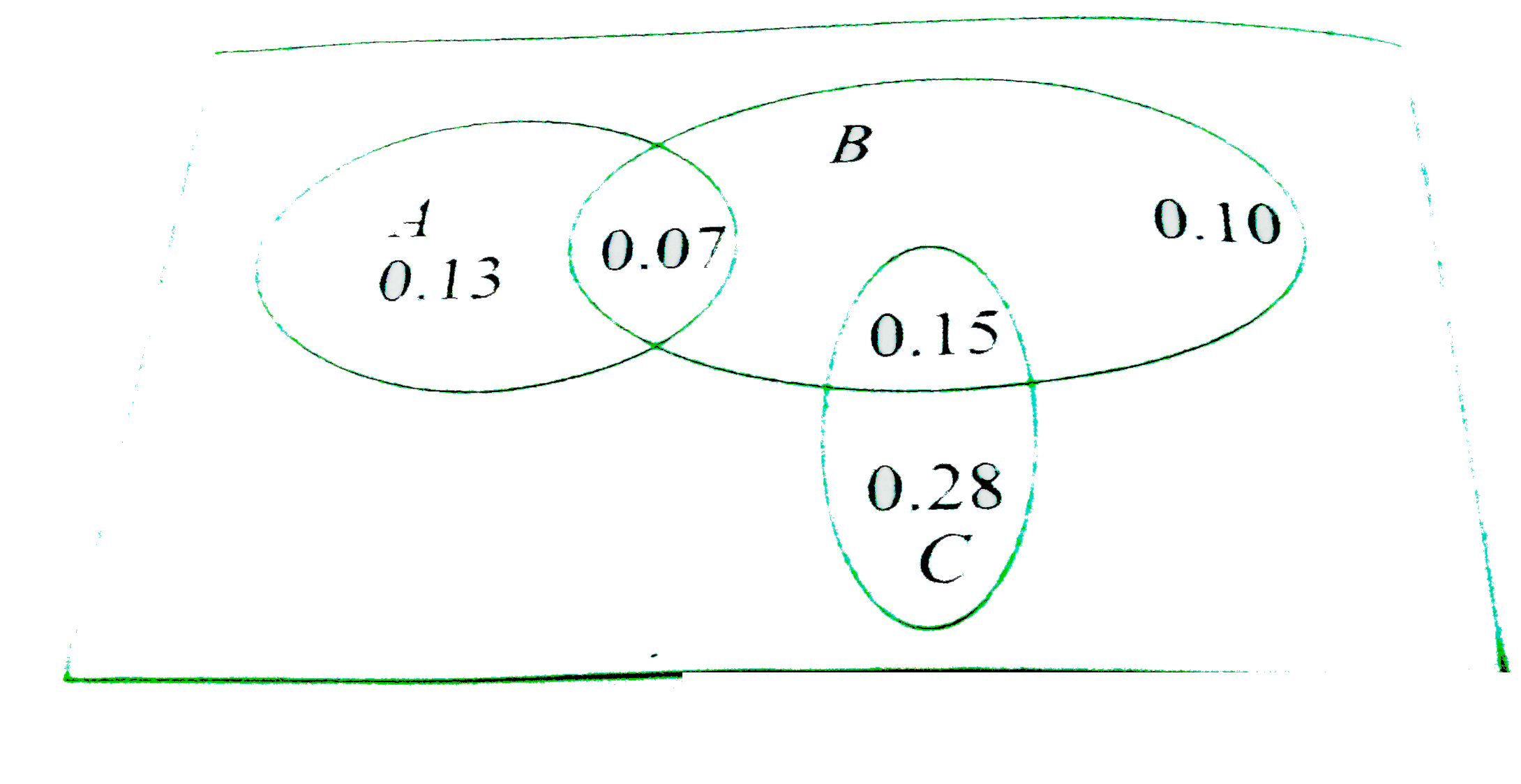
- The following Venn diagram shows three events, A, B, and C, and also t...
Text Solution
|
- Let omega be a complex cube root unity with omega!=1. A fair die is th...
Text Solution
|
- Three boys and two girls stand in a queue. The probability, that the n...
Text Solution
|
- Three randomly chosen nonnegative integers x , ya n dz are found to sa...
Text Solution
|
- Box 1 contains three cards bearing numbers, 1, 2, 3, box 2 contains fi...
Text Solution
|
- Box 1 contains three cards bearing numbers 1, 2, 3; box 2 contains fiv...
Text Solution
|
- PARAGRAPH A There are five students S1,\ S2,\ S3,\ S4 and S5 in a musi...
Text Solution
|
- There are five students S(1), S(2), S(3), S(4) and S(5) in a music cla...
Text Solution
|