Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ICSE-CHEMISTRY-2019-Question (Answer the following questions)
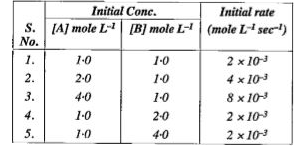
- For the reaction A + B to C + D, the initial rate for different react...
Text Solution
|
- Which trivalent ion has maximum size in the lanthanoid series i.e., L...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why: Cu^(+) " is diamagnetic but " Cu^(2+) is paramag netic...
Text Solution
|
- When a coordination compound CoCl(3).6NH(3) " is mixed with " AgNO(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the boiling point of urea solution when 6 g of urea is diss...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the compounds A, B, C and D in the given reaction : HC-=CH...
Text Solution
|