Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
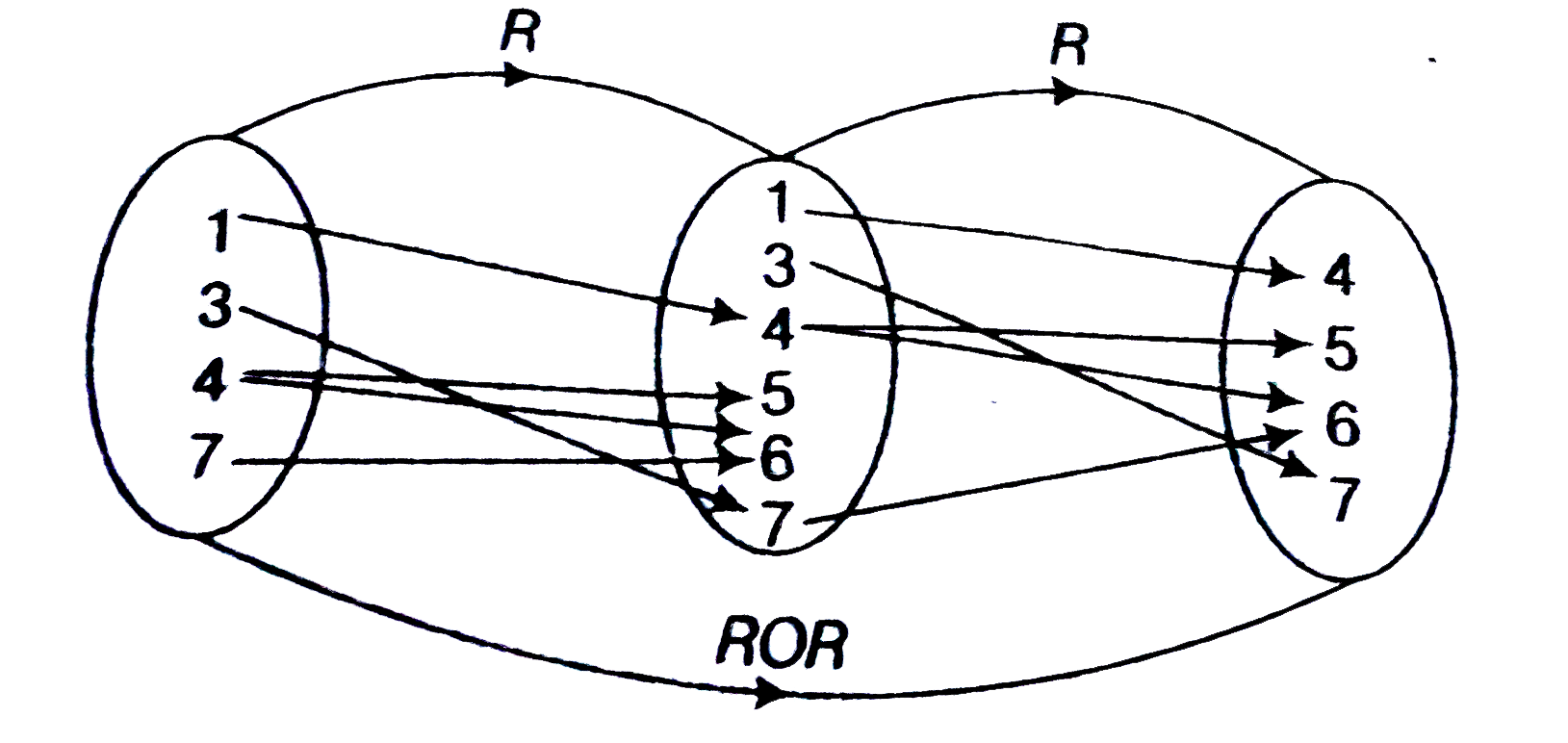
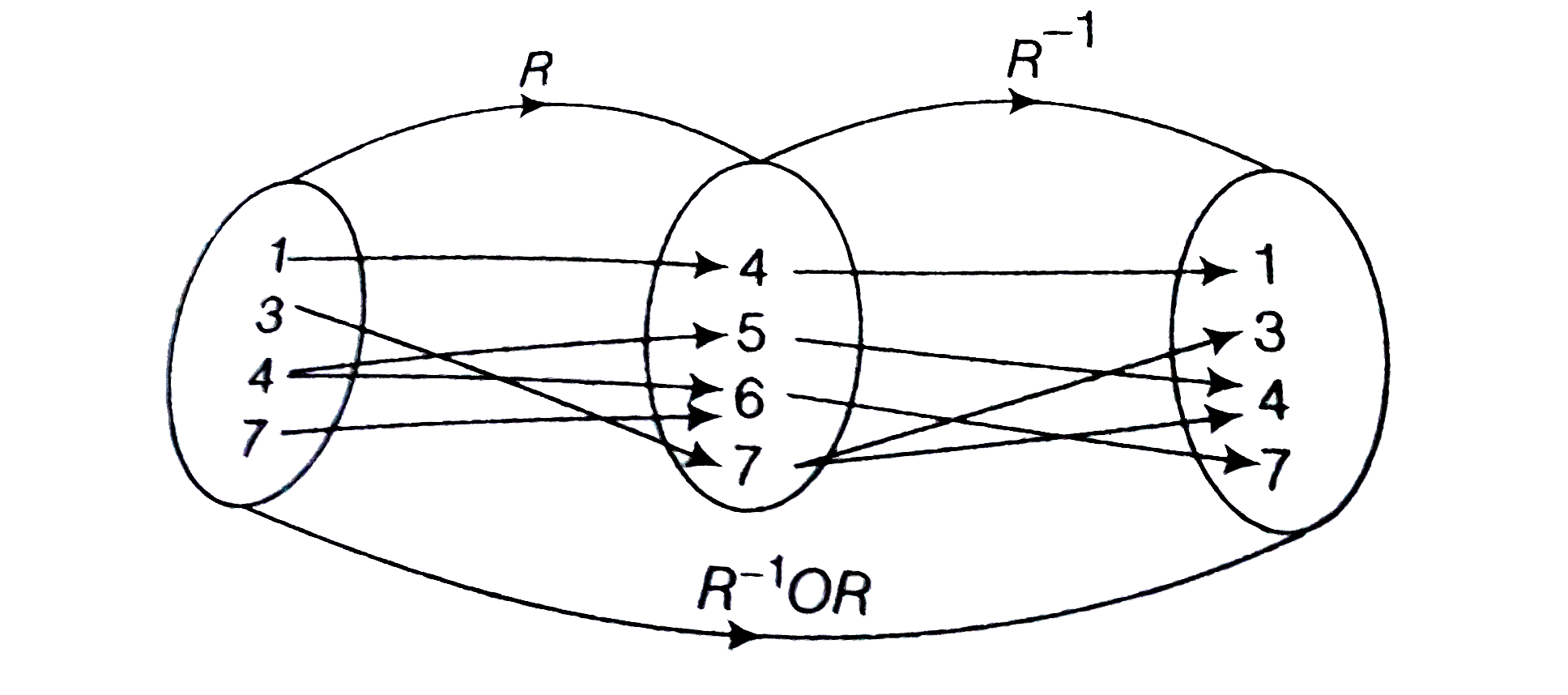
- Let R be a relation such that R = {(1,4), (3,7), (4,5), (4,6), (7,6)},...
Text Solution
|
- Let R be a relation defined by R={(9,8),(1,9),(9,6),(7,6),(2,7)} then ...
Text Solution
|
- Let a relation R be defined by relation The R={(4,5),(1,4),(4,6),(7,6)...
Text Solution
|
- Let R be a relation such that R={(1,4),(3,7),(4,5),(4,6),(7,6)}, then ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) If A= {x,y,z}, B=(1,2,3} and R= {(x,2),(y,3),(z,1),(z,2), then fin...
Text Solution
|
- यदि सम्बन्ध R इस प्रकार है कि R={(4,5),(1,4),(4,6),(7,6),(3,7)}, तो ...
Text Solution
|
- मान लीजिएः कोई सम्बन्ध R इस प्रकार परिभाषित है की- R={(4,5),(1,4),(...
Text Solution
|
- Let R be a relation such that R = {(1,4), (3,7), (4,5), (4,6), (7,6)},...
Text Solution
|
- यदि सम्बन्ध R इस प्रकार है कि R={(4,5),(1,4),(4,6),(7,6),(3,7)}, तो ...
Text Solution
|