Column-I gives certain situations involving two thin conducting shells connected by a conducting wire via a key K. In all situation one sphere has net charge +q and other sphere has no net charge. After the key K is pressed, column-II gives some resulting effect.
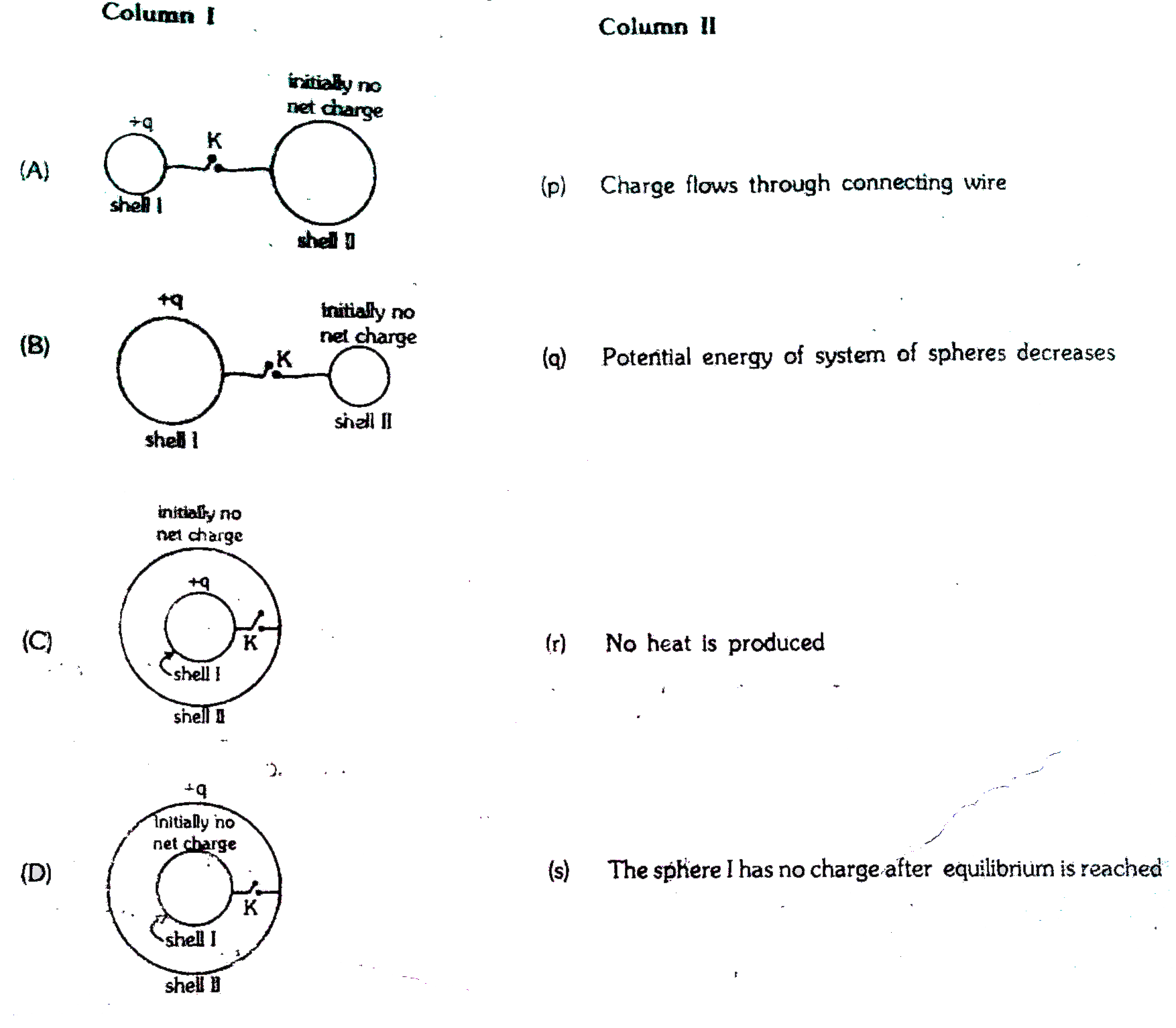
Column-I gives certain situations involving two thin conducting shells connected by a conducting wire via a key K. In all situation one sphere has net charge +q and other sphere has no net charge. After the key K is pressed, column-II gives some resulting effect.


Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
(A) p, q (B) p, q (C) p, q s (D) r, s
(A) Initially, the potential difference exist between both shells, so positive charge is flow from high to low potential.
Wvery system wants to acquire minimum potential energy if possible for stability. So charge flown to achieve it.
(B) As explained in [A], charge flow does not depends on the size of sphere.
(C) Charge flow through wire until the potential becomes same for both shells.
(D) Potential is same everywhere inside a conducting shell. So no charge is flow through connecting wire, so no heat is produced.
Wvery system wants to acquire minimum potential energy if possible for stability. So charge flown to achieve it.
(B) As explained in [A], charge flow does not depends on the size of sphere.
(C) Charge flow through wire until the potential becomes same for both shells.
(D) Potential is same everywhere inside a conducting shell. So no charge is flow through connecting wire, so no heat is produced.
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise Exersice-05|1 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise Exercise-06|1 VideosMISCELLANEOUS
ALLEN |Exercise Exersice-04|1 VideosKINEMATICS (MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE AND MOTION IN A PLANE)
ALLEN |Exercise BEGINNER S BOX-7|8 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD, UNITS AND DIMENSIONS & ERRORS IN MEASUREMENT
ALLEN |Exercise EXERCISE-IV|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
The two conducting spherical shells are joined by a conducting wire and cut after some time when charge stops flowing. Find out the charge on each sphere after that.
When two spheres having 4Q and - 2Q charge are placed at a certain distance, the force acting between them is F. Now they are connected by a conducing wire and again separated from each other. Now they are kept at a distance half of the previous one. The force acting between them is.......
Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to each other by a wire. What is the ratio of electric fields at the surfaces of the two spheres? Use the result obtained to explain why charge density on the sharp and pointed ends of a conductor is higher than on its flatter portions.
In the shown expermiental setup to study photoelectric effect, two conducting electrodes are enclosed in an evacuated glass-tube as shown. A parallel beam of monochromatic light, falls on photosensitive electrodes. The emf of battery shwon is high enough such that all photoelectron ejected from left electrode will reach the right electrode. Under initial conditions photoelectrons are emitted. AS changes are made in each situation of column-I, Match the statements in column-I with results in column-II. {:(,"Column I",,"Column II"),((A),"If frequency of incident light is increased keeping its intensity constant",(p),"magnitude of stopping potential"),((B),"If frequency of incident light is increased and its intensity is decreased",(q),"current through circuit may stop"),((C),"If work function of photo sensitive electrode is increased",(r),"maximum kinetic energy of ejected photoelectrons will increase"),((D),"If intensity of incident light is increased keeping its frequency constant",(s),"saturation current will increase"):}
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil slicks, show patterns of alternating dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected light waves. If two waves are in phase their crest and troughs will coincide. The interference will be constructive and the aplitude of the resultant wave will be greater than the amplitude of either constituent wave. if the two waves are out of phase, the crests of one wave will coincide with the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the amplitude of the resultant wave will be less than that of either constituent wave. at the interface between two transparent media some light is reflected and some light is refracted. * When incident light, reaches the surface at point a, some of the light is reflected as ray R_(a) and and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. *At point b some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back refracted out of the fiml as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has travelled the extra distance within the film of abc. if the angle of incidence is small then abc is approximately twice the film's thickness. if R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright if R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference. * Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. * For reflection at the interface between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1)ltn_(2) the reflected wave will change phase by pi . if n_(1)gtn_(2) the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. for reference n_(air)=1.00 * if the waves are in phase after refection at all interfaces, then the effects of path length in the film are Constructive interference occur when (n= refractive index) 2t=mlamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... .. Destructive interference occurs when 2t=(m+1//2)lamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... Q. A 600 nm light is perpendicularly incident on a soap film suspended in air. The film is 1.00 mum thick with n=1.35. Which statement most accurately describes the interference of the light reflected by the two surfaces of the film?
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil slicks, show patterns of alternating dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected light waves. If two waves are in phase their crest and troughs will coincide. The interference will be constructive and the aplitude of the resultant wave will be greater than the amplitude of either constituent wave. if the two waves are out of phase, the crests of one wave will coincide with the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the amplitude of the resultant wave will be less than that of either constituent wave. at the interface between two transparent media some light is reflected and some light is refracted. * When incident light, reaches the surface at point a, some of the light is reflected as ray R_(a) and and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. *At point b some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back refracted out of the fiml as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has travelled the extra distance within the film of abc. if the angle of incidence is small then abc is approximately twice the film's thickness. if R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright if R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference. * Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. * For reflection at the interface between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1)ltn_(2) the reflected wave will change phase by pi . if n_(1)gtn_(2) the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. for reference n_(air)=1.00 * if the waves are in phase after refection at all interfaces, then the effects of path length in the film are Constructive interference occur when (n= refractive index) 2t=mlamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... .. Destructive interference occurs when 2t=(m+1//2)lamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... Q. The average human eye sees colors with wavelengths between 430 nm to 680 nm. For what visible wavelength will a 350 nm thick n=1.35 soap film produce maximum destructive interference?
Two rectangular blocks, having identical dimensions, an be arranged either in configuration-I or in configuration-II as shown in the figure. One of the blocks has thermal conductivity k and the other 2k. The temperature difference between the ends along the x-axis is the same in both the configurations. It takes 9s to transport a certain amount of heat from the hot end to the cold end in the configuration-I. The time to transport the same amount of heat in the configuration-II is
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil show patterns of alternative dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected ligth waves. If two waves are in phase, their crests and troughs will coincide. The interference will be cosntructive and the amlitude of resultant wave will be greater then either of constituent waves. If the two wave are not of phase by half a wavelength (180^(@)) , the crests of one wave will coincide width the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the ampliutde of the resultant wave will be less than that of either consituent wave. 1. When incident light I, reaches the surface at point a, some of the ligth is reflected as ray R_(a) and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. 2. At point b, some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back through the film along path bc. At point c, some of the light is reflected back into the film and part is reflected out of the film as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has travelled the extra distance within the film fo abc. If the angle of incidence is small, then abc is approxmately twice the film's thickness . If R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase, they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright. If R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference and the region ac will be dark. I. Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. II. For reflection at the interfere between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1) gt n_(2) , the reflected wave will change phase. If n_(1) lt n_(2) , the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. For reference, n_(air) = 1.00 . III. If the waves are in phase after reflection at all intensities, then the effects of path length in the film are: Constrictive interference occurs when 2 t = m lambda // n, m = 0, 1,2,3 ,... Destrcutive interference occurs when 2 t = (m + (1)/(2)) (lambda)/(n) , m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... If the waves are 180^(@) out of the phase after reflection at all interference, then the effects of path length in the film ara: Constructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m + (1)/(2)) (lambda)/(n), m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... Destructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m lambda)/(n) , m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... A thin film with index of refraction 1.33 coats a glass lens with index of refraction 1.50. Which of the following choices is the smallest film thickness that will not reflect light with wavelength 640 nm?