Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN -CURRENT ELECTRICITY-EXERCISE-IV A
- By a cell a current of 0.9 A flows through 2 ohm resistor and 0.3 A th...
Text Solution
|
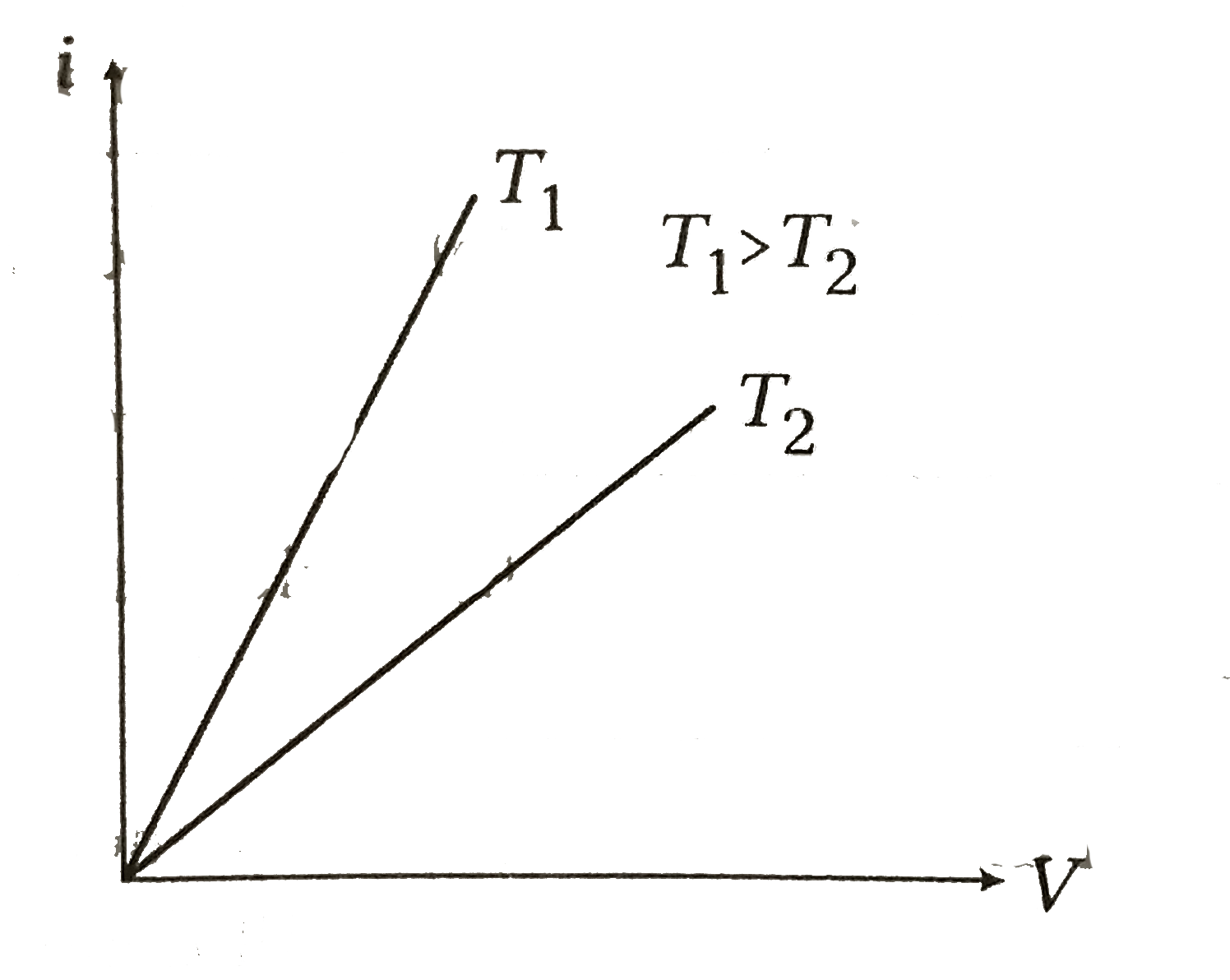
- Assertion : Current versus potential difference (i-V) graph for a cond...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer of resistance 100Omega gives full scale deflection for ...
Text Solution
|
- For changing the range of a galvanometer with G ohm resistance fromV v...
Text Solution
|
- The specific resistance of a conductor increases with:
Text Solution
|
- For a cell terminal potential difference is 2.2 V when circuit is open...
Text Solution
|
- N identical cells whether joined together in series or in parallel, gi...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference between the points A and B in the following c...
Text Solution
|
- Length of a potentiometer wire is kept long and uniform to ahcieve:-
Text Solution
|
- A body is projected up such that its position vector varies with time ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equivalent resistance across AB :
Text Solution
|
- There are three voltmeters of the same range but of resistance 10000 O...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit element given here, if the potential at point B = V(B) ...
Text Solution
|
- A copper wire has a square cross-section, 2.0 mm on a side. It carr...
Text Solution
|
- The emf of a battery is 2V and its internal resistance is 0.5Omega the...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference across the 100 Omega resistance in the follow...
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent resistance between the point P and Q in the network giv...
Text Solution
|
- When connected across the terminals of a cell, a voltmeter measures 5 ...
Text Solution
|
- Thirteen resistances each of resistance R ohm are connected in the cir...
Text Solution
|
- A group of N cells whose emf varies directly with the internal resista...
Text Solution
|