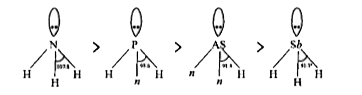Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ACCURATE PUBLICATION-BOARD PAPER MARCH - 2019-QUESTIONS
- 18 g of glucose is dissolved in 1 kg of water. At what temperature wil...
Text Solution
|
- State Henry's law and mention its some important applications.
Text Solution
|
- Why bond angle of Phosphine (PH3) is less than Ammonia (NH3) ?
Text Solution
|
- Why is H2S less acidic than H2 Te ?
Text Solution
|
- The molar conductivities at infinite dilution for sodium acetate, hydr...
Text Solution
|
- What is corrosion?
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the molar conductance of solutions of MgCl2 at infinite dil...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Give two differences between emf and potential difference. (ii) ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Reimer Tiemann reaction with one example.
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert chlorobenzene into phenol ?
Text Solution
|
- Why Phenols are more acidic than Alcohol ?
Text Solution
|
- Write two differences between physical adsorption and chemical adsorpt...
Text Solution
|
- Define Emulsion
Text Solution
|
- Write Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Why are the boiling points of carboxylic acids higher than the corresp...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophi...
Text Solution
|
- A face centered cubic element (atomic mass =60) has edge length of 400...
Text Solution
|
- Give one difference between crystalline and amorphous solids.
Text Solution
|
- An element having a density 11.2"g cm"^(-3) forms a fcc lattice with e...
Text Solution
|
- Define unit cell and paramagnetic substance.
Text Solution
|