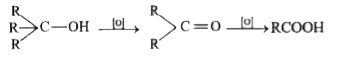
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACID & THEIR DERIVATIVES
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-III (Single Correct Answer Type)|10 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACID & THEIR DERIVATIVES
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-III (Multiple Correct Answer Type)|10 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACID & THEIR DERIVATIVES
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-III (Linked Comprehension Type)|12 VideosBIOMOLECULES, POLYMERS AND CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-II (ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS)|6 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION|Exercise LEVEL-II (Assertion -Reason)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BRILLIANT PUBLICATION-CARBOXYLIC ACID & THEIR DERIVATIVES-LEVEL-II
- Tertiary alcohols (3^(@)) having at least four carbon atoms upon drast...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction, C(6)H(5)OH overset(NaOH)to (A) underset(140^(@)C,(4-7...
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acid group does not give the usual addition and elimination...
Text Solution
|
- In a set of the given reactions, acetic acid yielded a product C. C...
Text Solution
|
- The correct order of increasing acid strength of the following compoun...
Text Solution
|
- alpha-Hydroxypropanoïc acid can be prepared from ethanal by following ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following methods give a carboxylic acid without homologa...
Text Solution
|
- In which case number of carbon atoms is retained?
Text Solution
|
- Select the incorrect statement.
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reactions, I. II. CH(3)CH(2)Br overset(...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following compounds will react with NaHCO(3) solution...
Text Solution
|
- CH(2)=CH(CH(2))(2)COOH and HBr reacts in presence of peroxide to give
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following types of hydrolysis of esters give directly car...
Text Solution
|
- Why the aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reacti...
Text Solution
|
- . The product Y is :
Text Solution
|
- A hydrocarbon C(6)H(12) decolourises bromine and gives n-Hexane on hyd...
Text Solution
|
- underset((A))(PhMe) underset(Delta,H(3)O^(o+))overset(KMnO(4)// overse...
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acid, although unreactive to alcohols, reacts in the presen...
Text Solution
|
- The acid D obtained through the following sequece of reactions is C(2...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following presents the correct order of the acidity in th...
Text Solution
|