Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-QUESTIONS
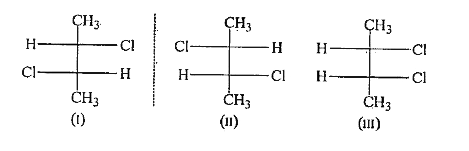
- Give different Enantiomers of 2 chlorobutane.
Text Solution
|
- Give different Enantiomers of 3-methyl hexane.
Text Solution
|
- State and explain the term diastereoisomers and mesomers.
Text Solution
|
- What is racemisation ?
Text Solution
|
- Define asymmetric synthesis.
Text Solution
|
- Point out the difference between : Chirality and chiral centre (or c...
Text Solution
|
- Point out the difference between : Enantiomers and diastereomers.
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between recemic mixture and meso compound .
Text Solution
|
- Define inversion.
Text Solution
|
- Define retention.
Text Solution
|
- The p-isomer of dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than O-and M-...
Text Solution
|
- The p-isomer of dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than O-and M-...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons : Boiling point of alkyl bromide is higher than alkyl c...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons : Alkyl halides are better solvents than aryl halides.
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons : Haloalkanes used as solvents in industry are chloro ...
Text Solution
|
- What are ambident uncleophiles ? Explain with an example.
Text Solution
|
- Alkyl Chloride is more reactive than chlorobenzene towards nucleophili...
Text Solution
|
- With the help of polarity of the carbon halogen bond show that aryl ha...
Text Solution
|
- Why are haloarenes more stable than haloalkanes ?
Text Solution
|
- Why do alkyi haldies undergo hydrolysis more readily than aryl halides...
Text Solution
|