Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise SHORT ANSWERTYPE QUESTIONS|13 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|8 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS|26 VideosELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise Most Expected Questions|7 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICALS|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
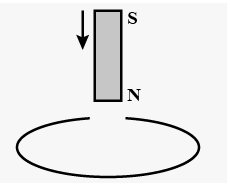
- A copper ring is held horizontally and a bar magnetic is dropped throu...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why resistance coils are usually double wound.
Text Solution
|
- Show that Lenz's law is a direct consequence of the law of conservatio...
Text Solution
|
- Show that Lenz's law obeys the law of conservation of energy.
Text Solution
|
- What is electromagnetic induction ? Write its Faraday's laws ?
Text Solution
|
- What are eddy currents ? How are these produced ? How eddy currents ca...
Text Solution
|
- What are eddy currents ? How are these produced ? How eddy currents ca...
Text Solution
|
- An induced current has no direction of its own. Explain, why?
Text Solution
|
- Why is the coil of a dead beat galvanometer wound on a metal frame?
Text Solution
|
- Self-induction is called inertia of electricity. Explain why.
Text Solution
|