A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SAMPLE PAPER 2022
CBSE MODEL PAPER|Exercise ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS(SECTION A)|4 VideosSAMPLE PAPER 2022
CBSE MODEL PAPER|Exercise ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS(SECTION B)|3 VideosSAMPLE PAPER 2022
CBSE MODEL PAPER|Exercise SECTION - B|9 VideosSAMPLE PAPER (MATHEMATICS STANDARD)
CBSE MODEL PAPER|Exercise PART - B|16 VideosSAMPLE PAPER 2022 TERM II
CBSE MODEL PAPER|Exercise SECTION C|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CBSE MODEL PAPER-SAMPLE PAPER 2022-SECTION - C
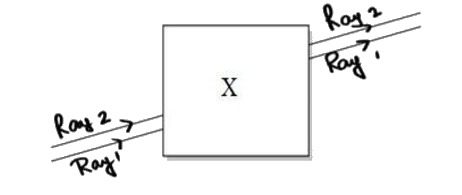
- Noor, a young student, was trying to demonstrate some properties of li...
Text Solution
|
- Noor, a young student, was trying to demonstrate some properties of li...
Text Solution
|
- Noor, a young student, was trying to demonstrate some properties of li...
Text Solution
|
- Noor, a young student, was trying to demonstrate some properties of li...
Text Solution
|