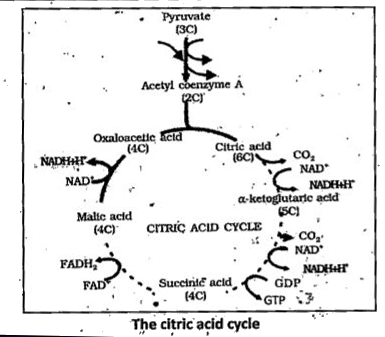
The reaction sequence of Kreb.s cycle is as below.
1. Condensation : Acetyl co-enzyme A condenses with oxaloacetic acid and results in the formation of citric acid and co-enzyme-A. This condensation reaction is catalysed by the enzyme .citric synthetase.
Oxaloacetic acid + Acetyl CoA `overset("Citric Synthetase")rarr` Citric acid + Coenzyme A.
2. Dehydration : The enzyme .aconitase. catalyses the removal of one molecule of water from citric acid leading to the formation of cis-aconitic acid.
Citric acid `overset("Aconitase")rarr` Cis - aconitic acid + `H_2O`
3. Hydration : Addition of one molecule of water is done in the presence of aconitase Cis-aconitic acid forms Isocitric acid.
Cis-aconitic acid `+H_2O overset("Aconitase")rarr` isocitric acid.
4. Oxidation - I : Isocitric - acid undergoes dehydrogenation (oxidation) in the presence of .isocitric dehydrogenase. enzyme, leading to the formation of oxalosuccinic acid. In this reaction NAD is reduced to NADH + `H^+`.
Isocitric acid + NAD + `overset("isocitric dehydrogenase")rarr` Oxalosuccinic acid `+ NADH +H^(+)`
5. Decarboxylation : Oxalosuccinic acid releases one molecule : of `CO_2` in the presence of oxalosuccinic decarboxylase enzyme and forms `alpha` ketoglutaric acid.
Oxalosuccinic acid `overset("Oxalosuccinic decarboxylase")rarralpha` -ketoglutaric acid. `+CO_2`
6. Oxidation - II : `alpha` - ketoglutaric acid undergoes oxidation (dehydrogenase) decarboxylation and condensation with one molecule of CoA leading to the formation of succinyl coenzyme A.
`alpha` - Ketoglutaric acid + NAD + Coenzyme A `overset(alpha - "ketoglutaric dehydrogenase") rarr`
` rarr ` Succinyl conenzyme `A+ NADH + CO_2`
7. Cleavage : Succinyl coenzyme A splits into succinic acid and coenzyme A by the enzyme activity of succinic acid thiokinase. Energy released in this reaction is utilised to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Succinyl coenzyme A + ADP + Pi `overset("Succinic thiokinase")underset("Succinic acid + ATP + CoA")rarr`
8. Oxidation II : Succinic acid then undergoes oxidation and forms Fumeric acid. Instead of `NAD^(+)` , FAD serves as hydrogen acceptor in this reaction. Therefore FAD is reduced to FADH,. The enzyme which catalyses this reaction is known as succinic dehydrogenase.
Succinic acid `+ FAD overset("Succinic dehydrogenase ")rarr` Fumeric acid `+FADH_2`
9 Hydration: The enzyme Fumerase mediates the addition of one water molecule to fumeric aicd leads to the formation of malic aicd.
Fumeric acid `H_2Ooverset("Fumerase")rarr` Malic acid.
10. Oxidation IV : In the presence of Malic dehydrogenase, Malic acid releases two hydrogen atoms and gives rise to oxaloacetic .acid. In this step `NAD^(+)` acts as hydrogen acceptor and is y converted into NADH `+ H^(+)`
, Malic acid + NAD + `overset("Malic dehydrogenase")rarr` Oxaloacetic acid `+ NADH+H^(+)`