Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VGS PUBLICATION-BRILLIANT-MODEL PAPER 7-SECTION-B
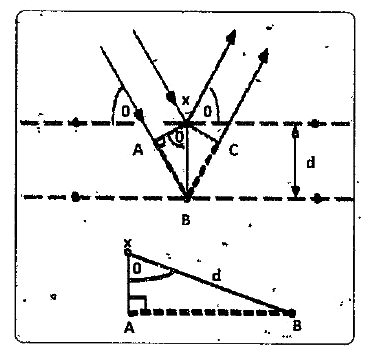
- Derive Bragg's equation .
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the mole fraction of H(2)SO(4) in a solution containing 98% ...
Text Solution
|
- What is catalysis ? How is catalysis classified ? Give two examples fo...
Text Solution
|
- Give examples to differentiate roasting and calcination.
Text Solution
|
- Explain ionic bond with suitable example.
Text Solution
|
- Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polyme...
Text Solution
|
- What are Hormones ? Give one example for each. i) Steroid Hormones ...
Text Solution
|
- What are Hormones ? Give one example for each. i) Steroid Hormones ...
Text Solution
|
- What are Hormones ? Give one example for each. i) Steroid Hormones ...
Text Solution
|
- How do you prepare Ethyl cyanide and Ethyl isocyanide from a common al...
Text Solution
|