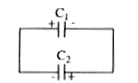
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CAPACITORS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE - III) (LEVEL - II (ADVANCED)) (More than One correct answer Type Questions)|7 VideosCAPACITORS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE - III) (LEVEL - II (ADVANCED)) (Linked Comprehension Type Questions)|6 VideosCAPACITORS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE - II) (LEVEL - II (ADVANCED)) (Straight Objective Type Questions)|5 VideosATOMS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE EXERCISE|21 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LECTURE SHEET (LEVEL - I) (MAIN) (EXERCISE - IV) (Straight Objective & More than one Correct Answer Type Questions)|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-CAPACITORS -PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE - III) (LEVEL - I (MAIN)) (Straight Objective Type Questions)
- A condenser of capacity 16 mF charged to a potential of 20 V is connec...
Text Solution
|
- A 4muF capacitor is charged by a 200 V battery. It is then disconnecte...
Text Solution
|
- A charged sphere is connected to a similar uncharged sphere. Then the ...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in increasing the P.D. across the plates of a capacitor ...
Text Solution
|
- A 10muF capacitor and a 20muF capacitor are connected in series across...
Text Solution
|