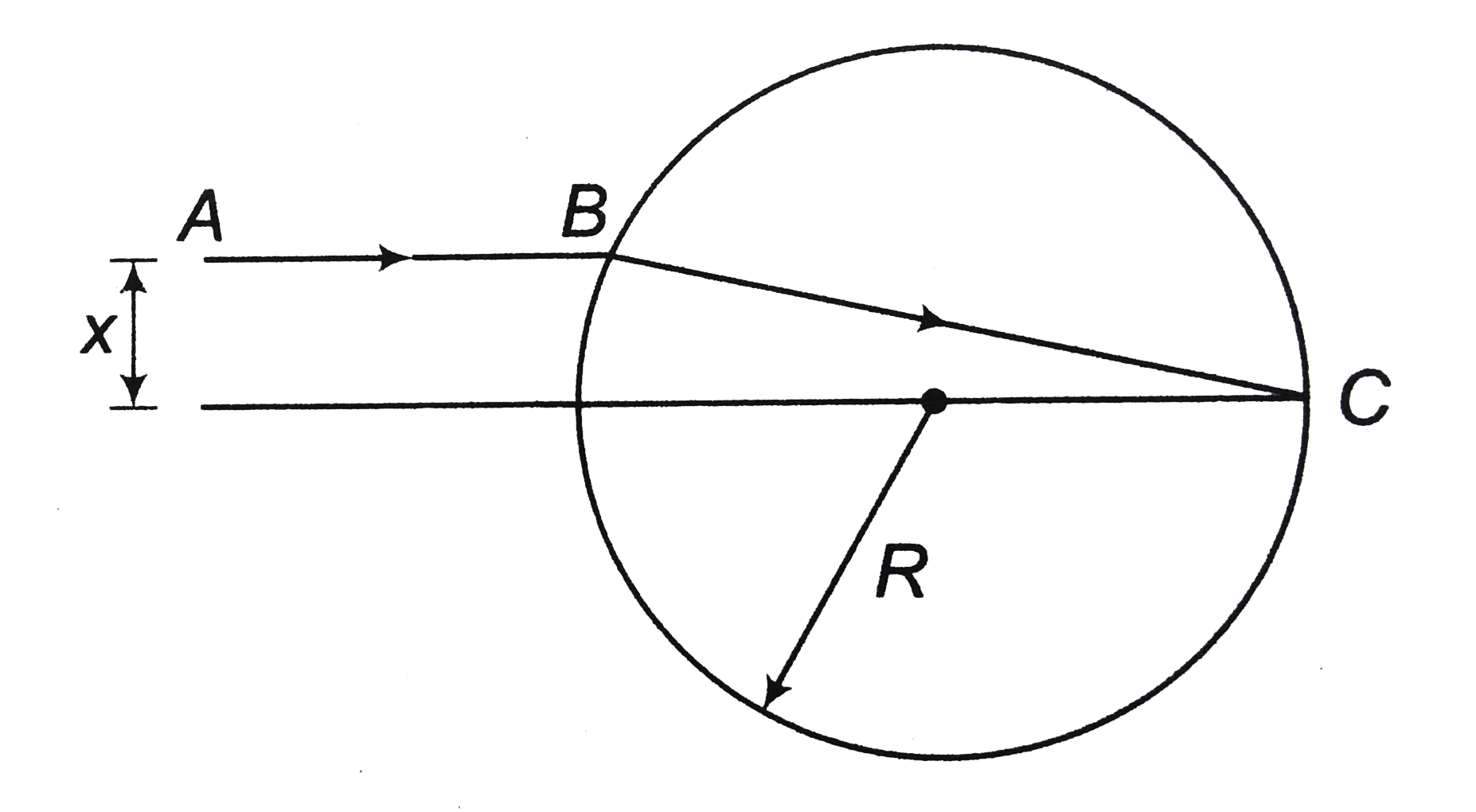
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (Section - H) Multiple True-FalseType Questions|3 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (Section - I) Subjective Type Questions|6 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment (Section - F) Matrix-Match Type Questions|2 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (Section-B)|5 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS (MATERIAL, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRUITS )
AAKASH INSTITUTE|Exercise Assignment SECTION - D (Assertion & reason type Question)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems