Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Molar And Equivalent Conductivity
Text Solution
|
- Molar And Equivalent Conductivity
Text Solution
|
- मोलर चालकता तथा तुल्यांकी चालकता की परिभाषा देने हुए इनकी इकाइयाँ लिखि...
Text Solution
|
- किसी विलयन की मोलर चालकता इसकी विशिष्ट चालकता से किस प्रकार सम्बन्धित ...
Text Solution
|
- किसी विलयन की मोलर चालकता सदैव इसकी तुल्यांक चालकता के समान होती है ।
Text Solution
|
- चालकता, तुल्यांकी चालकता एवं मोलर चालकता पर तनुता के प्रभाव को समझाइये...
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of dilution on the molar and equivalent conductance...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss (a) molar conductance and (b) equivalent conductance.
Text Solution
|
- Define conductance , speific conductance , molar conductivity and equi...
Text Solution
|
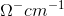 = mho. cm-1 (C.G.S system)
= mho. cm-1 (C.G.S system)