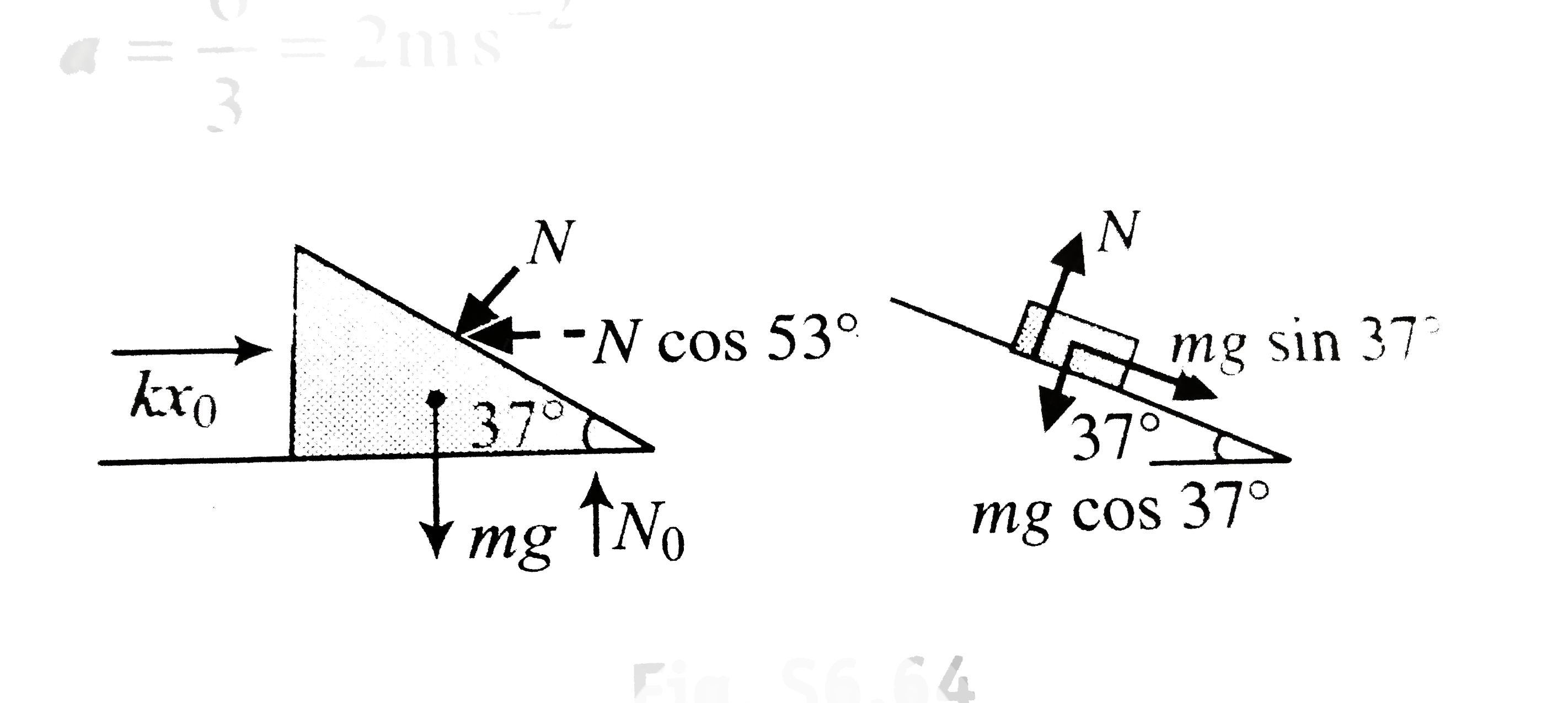Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Subjective|15 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Single Correct|76 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 6.3|19 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 VideosNEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-NEWTON'S LAWS OF MOTION 1-Exercise 6.4
- (a) A 10-kg block is supported by cord that runs to a spring scale, w...
Text Solution
|
- What is the reading of the spring balance in the following device?
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. three identical massless springs are kept horizontal. The left...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth block of mass m is connected with a spring of stiffness k(=20...
Text Solution
|
- A sand bag of mass m is hanging from a light spring of stiffness k. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of same mass m attached with a light spring are su...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 20 kg is suspended through two light spring balances a...
Text Solution
|
- Two block are connected by a spring of natural length 2m. The force co...
Text Solution
|
- If the force constant of spring is 50Nm^(-1), find mass of the block, ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of same mass m attached with a light string are su...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of 3kg mass when acceleration of 2kg mass is ms^...
Text Solution
|
- Find the reading of spring balance as shown in fig. Assume that mass M...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses m(1) and m(2) are in equilibrium. The block m(2) h...
Text Solution
|