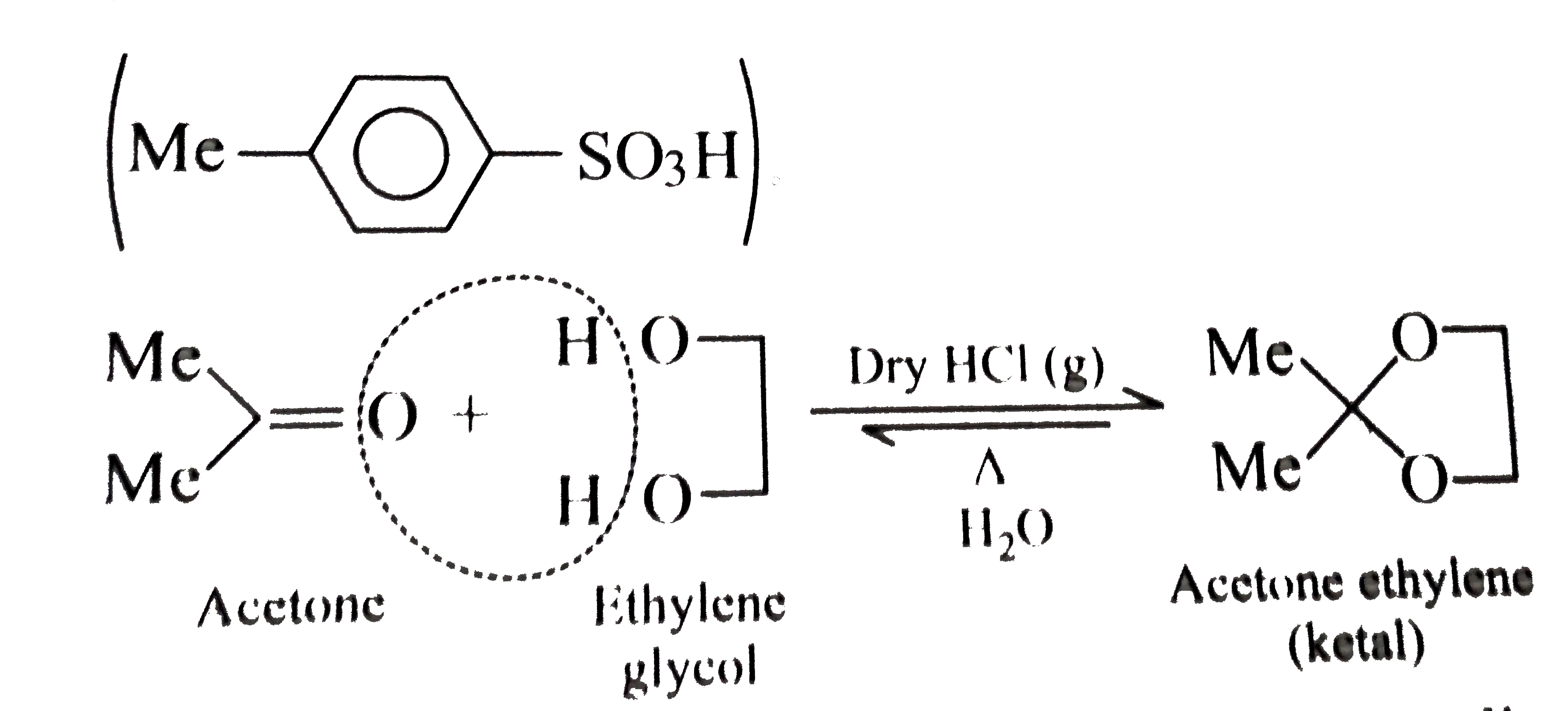
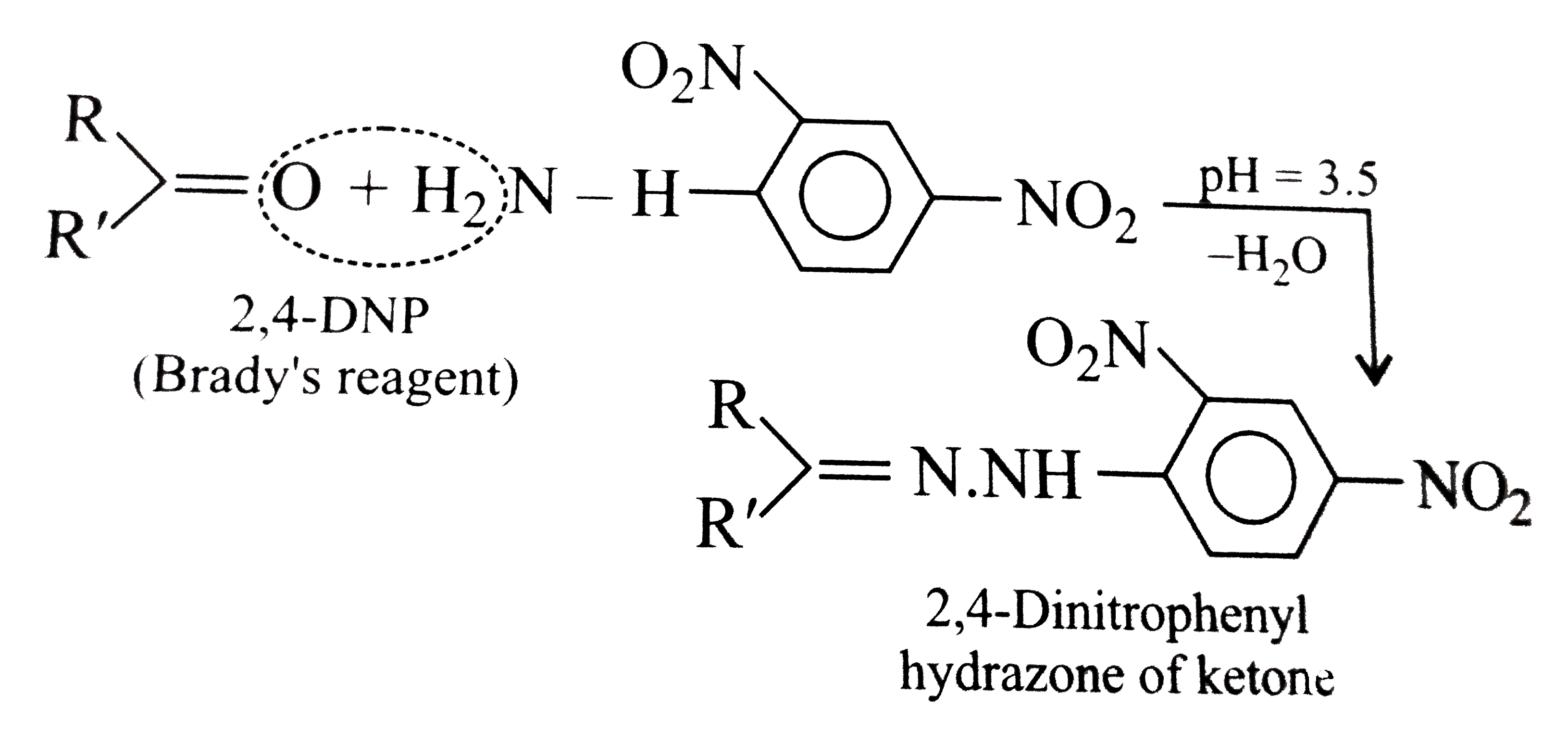
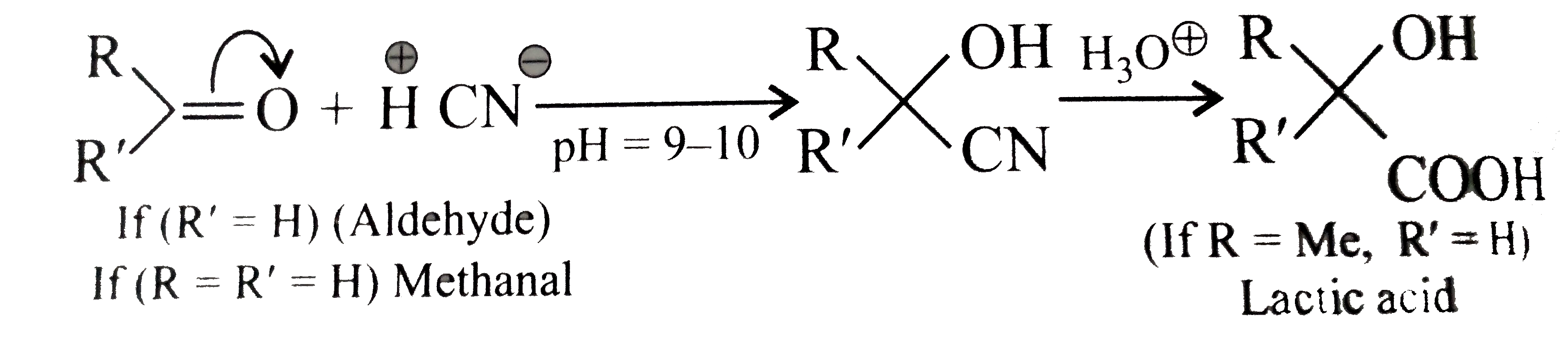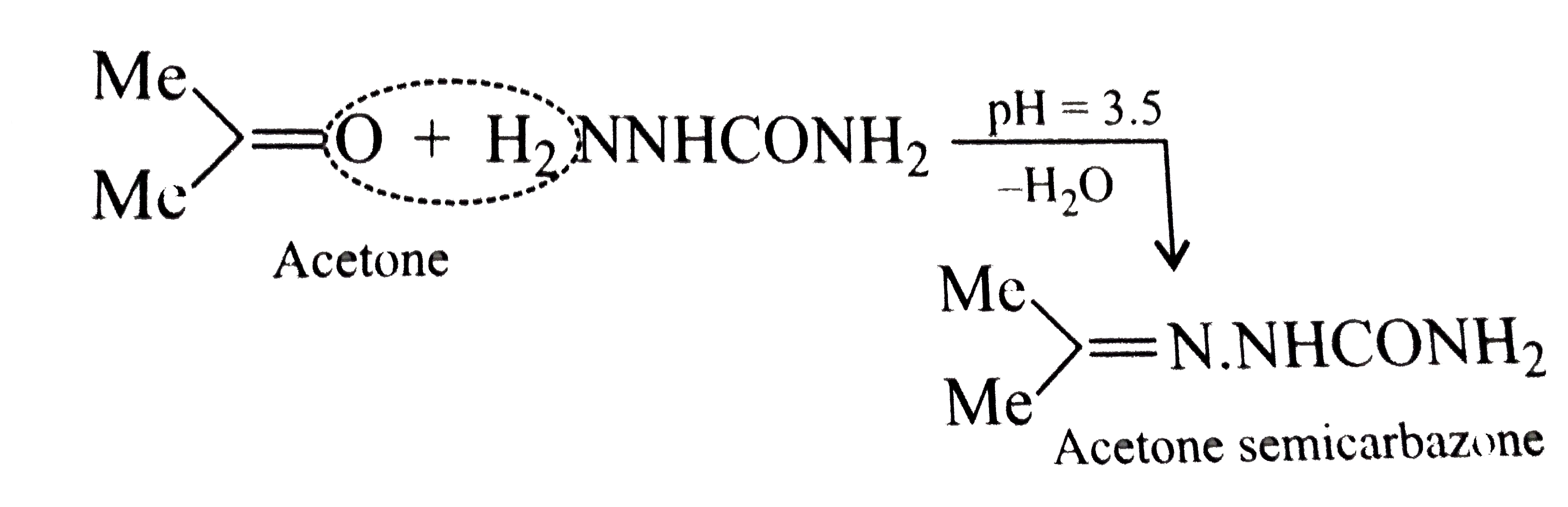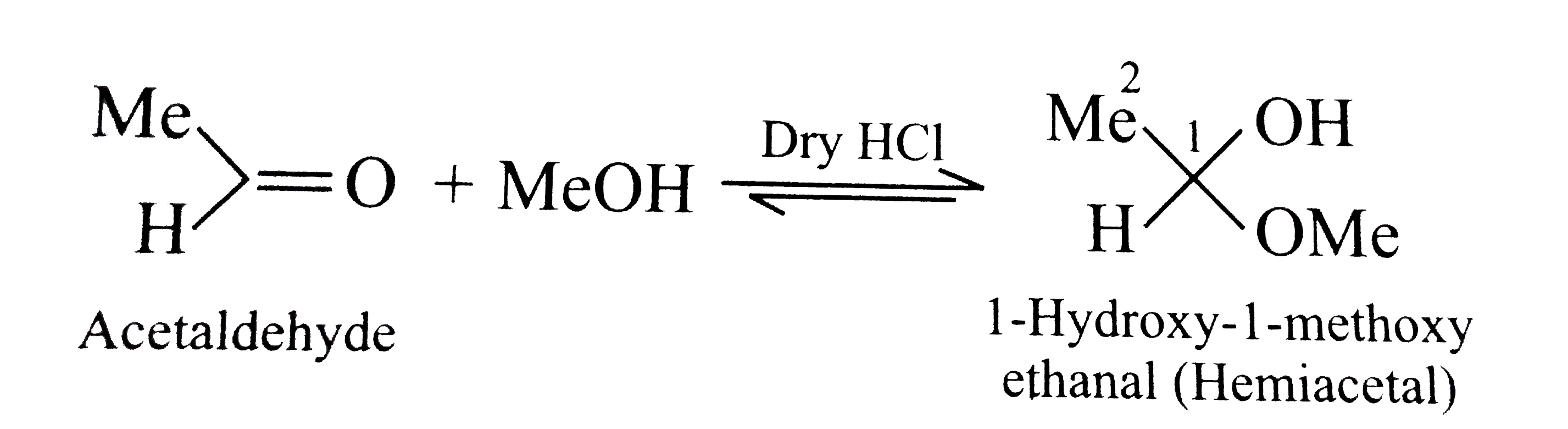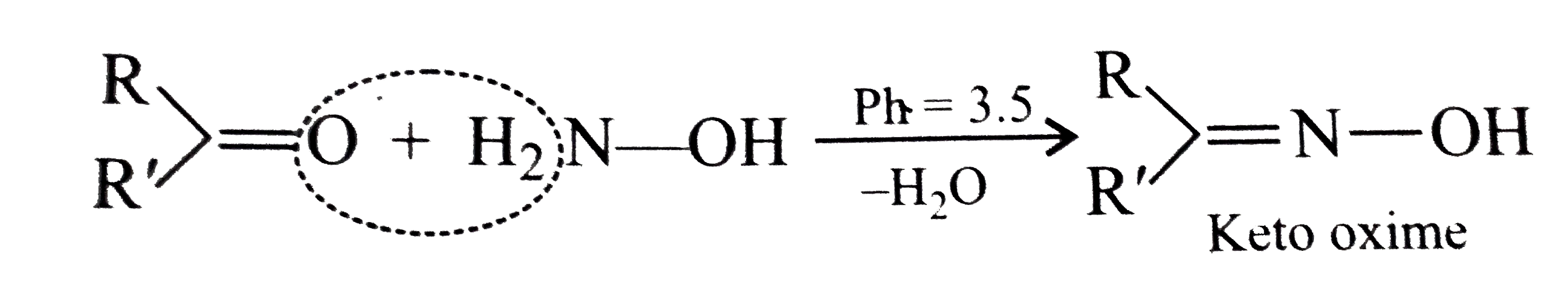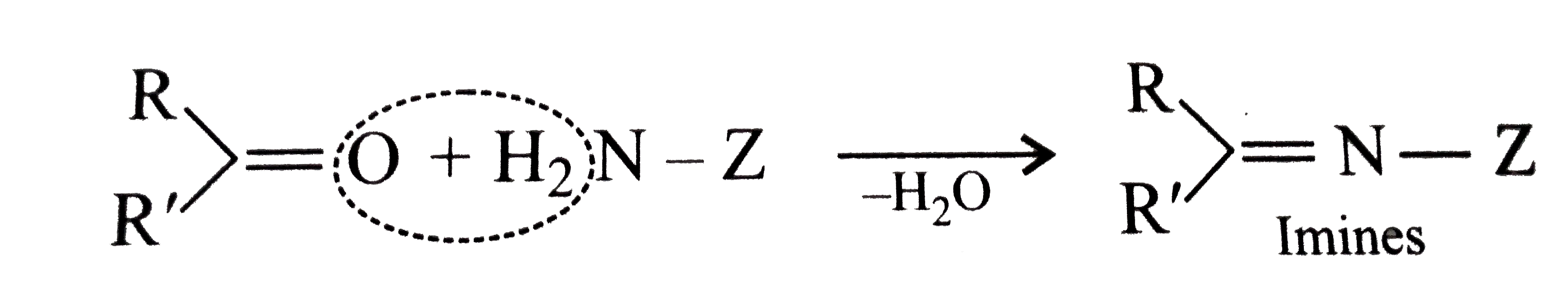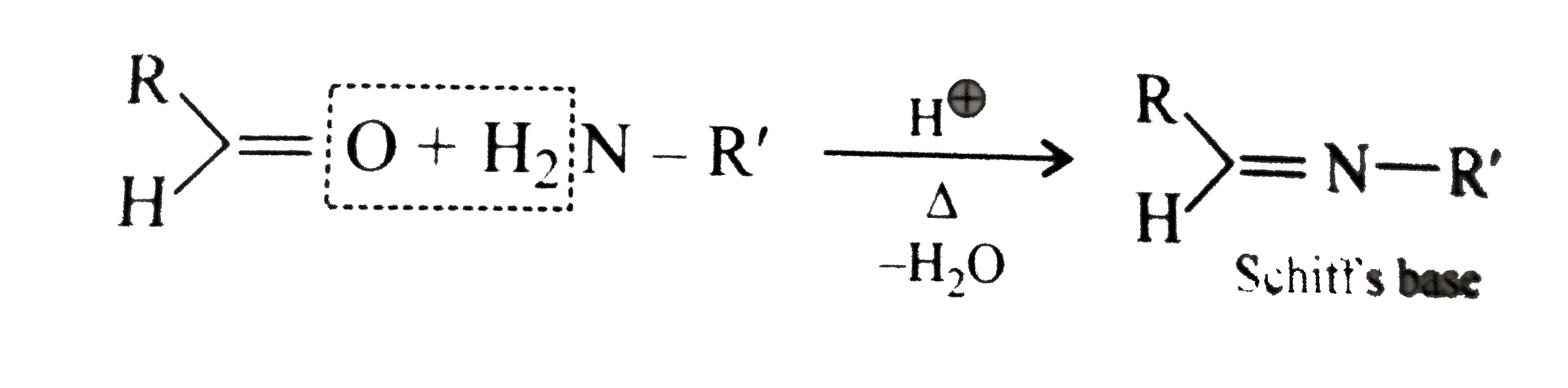Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Linked Comprehension|59 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Multiple Correct|40 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Subjective|52 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Analytical And Descriptive|15 VideosAMINES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise QUESTION BANK|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES-Exercises Concept Application
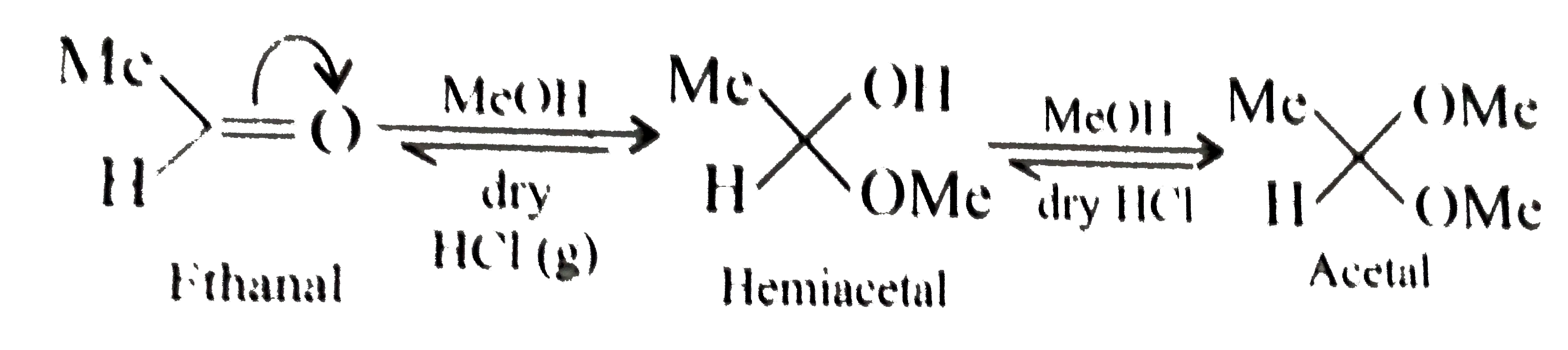
- What is meant by the following terms ? Give an example of the reaction...
Text Solution
|
- Name the following compounds according to the IUPAC system of nomencla...
07:29
|
- Draw the structures of following compound: i. 3-Methylbutanal ii. ...
05:34
|
- Write the IUPAC names of following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever pos...
06:03
|
- Draw the structure of following derivatives: i. 2,4-Dinitrophylhydra...
05:33
|
- Predict the products formed when cyclohexane carbaldehyde reacts with ...
05:21
|
- Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation or t...
12:57
|
- How will you convert ethnal into the following compounds ? i. Butane...
03:13
|
- Write structure formulae and names of four possible aldol condensation...
07:30
|
- An organic compound with the molecular folmula C(9)H(10)O form 2,4-DNP...
06:23
|
- An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C(8)H(16)O(2)) was hydrolys...
05:30
|
- Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their prope...
10:20
|
- Give simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs o...
07:06
|
- How will you prapare the following compounds from benzene ? You may us...
09:27
|
- How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than tw...
12:39
|
- Describe the following i. Acetylation ii. Cannizzaro reaction i...
08:27
|
- Complete each synthesis by giving the missing starting material, reage...
Text Solution
|
- Giving plausible explanation for each of the following: i. Cyclohexa...
04:10
|
- An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen, and rest ...
06:04
|
- Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than c...
01:26
|