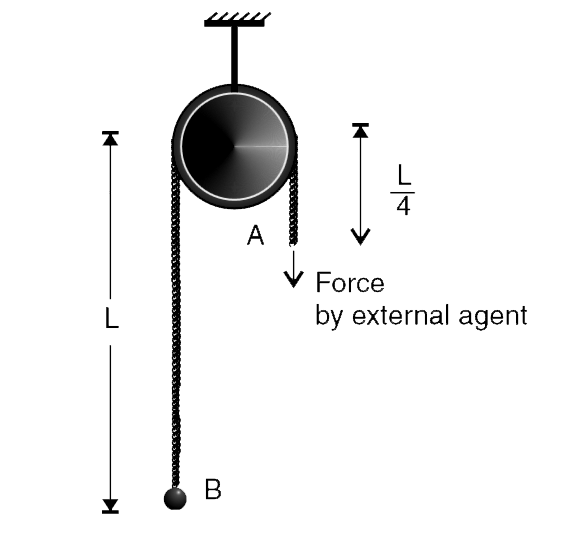
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT-WORK, POWER AND ENERGY-All Questions
- A mass of 2.0 kg is put on a flat pan attached to a vertical spring fi...
Text Solution
|
- A snake of mass M and length L is lying on an incline of inclination 3...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rope of linear mass density lambda (kg/m) passes over a smoo...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m = 100 g is projected vertically up with a kinetic...
Text Solution
|
- A physics student writes the elastic potential energy stored in a spri...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m = 4 kg is kept on an incline connected to a spring (...
Text Solution
|
- A body is projected directly up a plane which is inclined at an angle ...
Text Solution
|
- A tanker filled with water starts at rest and then rolls, without any ...
Text Solution
|
- A stone with weight W is thrown vertically upward into air with initia...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m = 0.1 kg is attached to the end B of an elastic string AB wit...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks 1 and 2 start from same point A on a smooth slide at the sa...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in the figure, block B of mass M rests on a w...
Text Solution
|
- In an aircraft carrier warship the runway is a 20 m long strip inclin...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass M is placed on a horizontal surface having coefficient...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is made to slide, starting from rest, along two equally ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle can move along x axis under influence of a conservative for...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is constrained to move along x axis under the action of a c...
Text Solution
|
- A pillar having square cross section of side length L is fixed on a sm...
Text Solution
|
- (i) A simple pendulum consist of a small bob of mass m tied to a strin...
Text Solution
|
- AB is a mass less rigid rod of length 2l. It is free to rotate in vert...
Text Solution
|