Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practive Exercise 5.4|11 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practive Exercise 5.5|12 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practive Exercise 5.2|6 VideosELECTROSTATICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numberical Problems|73 VideosHEAT AND THERMAL EXPANSION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise UNSOLVED NUMRICAL PROBLEMS FOR PREPARATION OF NSEP, INPhO & IPhO|82 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Practive Exercise 5.3
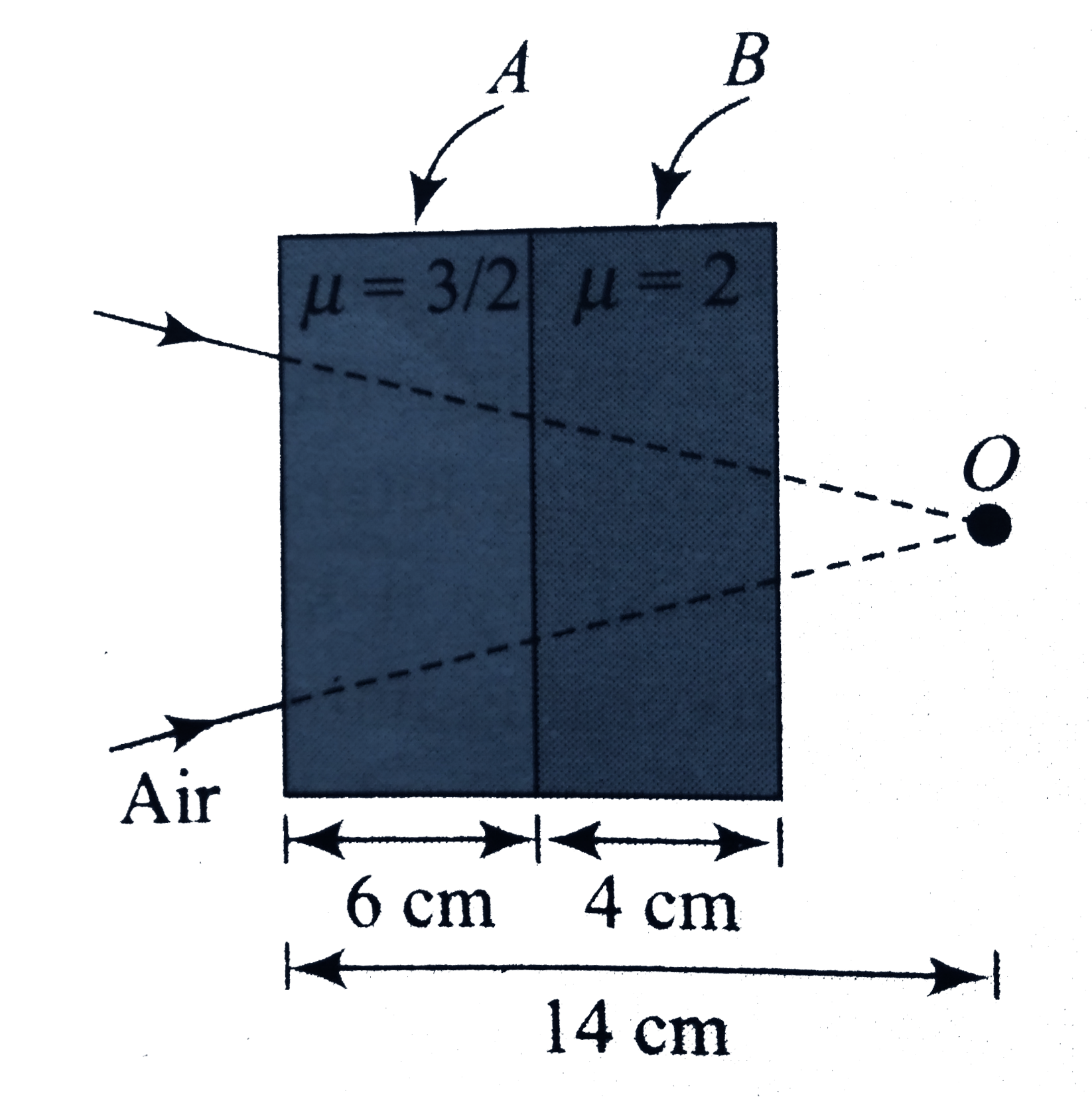
- A convergent beam is incident on two slabs placed in contact as showni...
Text Solution
|
- Find the apparent depth of an object O placed at the bottom of a beak...
Text Solution
|
- A point object is placed 33cm from a convex mirror of curvature radiu...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray falling at 60^(@) angle with the surface of fa glass slab ...
Text Solution
|
- A surveyor on one bank of canal observed the image of the 4 inch and ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a parallel slab of thickness t and refra...
Text Solution
|
- How much water should be filled in a container of height 21 cm, so tha...
Text Solution
|
- A glass plate has a thickness t and refravtive index mu A light ray is...
Text Solution
|
- A man standing on the edge of the swimming pool looking at a stone lyi...
Text Solution
|
- In a river 2m deep a water level measuring post embedded into the rive...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror of radius of curvature one meter is placed at the bot...
Text Solution
|
- A small object is placed at the centre of the bottom of a cylindrical ...
Text Solution
|