Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practive Exercise 5.5|12 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practive Exercise 5.6|16 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Practive Exercise 5.3|12 VideosELECTROSTATICS
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise Unsolved Numberical Problems|73 VideosHEAT AND THERMAL EXPANSION
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA|Exercise UNSOLVED NUMRICAL PROBLEMS FOR PREPARATION OF NSEP, INPhO & IPhO|82 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PHYSICS GALAXY - ASHISH ARORA-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS-Practive Exercise 5.4
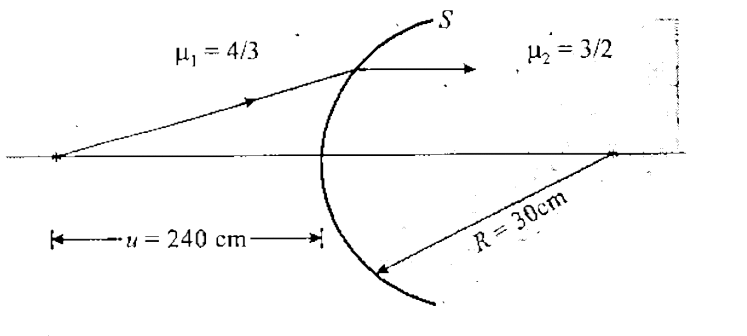
- A spherical surface S separates two media 1 and 2 as shown in figure ....
Text Solution
|
- A glass sphere of radius 5 cm has a small bubble at a distance 2 cm fr...
Text Solution
|
- A ray is incident on a glass sphere as shown.The opposite surface of t...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel incident beam falls on a solid glass sphere at near normal ...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere of glass of inner and outer radii R and 2R respectivel...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent sphere of radius R ahs a cavity of radius R//2 as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray incident at a point at an angle of incidence of 60^(@) enters a ...
Text Solution
|
- A glass sphere(mu=1.5) with a radius of 15.9 cm has a tiny air bubble ...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical beam of light of cross sectional radius (R)/(2) is inci...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a fish bowl of radius 10 cm in which along a diametrical ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec sqrt(2...
Text Solution
|