As we know that, the reactions
`2Na(s)+Cl_(2)(g)to2NaCl(s)`
`4Na(s)+O_(2)(g)to2Na_(2)(s)`
are redox reaction because in each of these reactions sodium is oxidised due to the addition of either oxygen or more electronegative element to sodium. Simultaneously, chlorine and oxygen are reduced because of each of these, the electropositive element sodium has been added. From our knowledge of chemical bonding we also know that, sodium chloride and sodium oxide are ionic compounds and perhaps better written as `Na^(+)Cl^(-)(s)` and `Na^(+)0_(2)O^(2-)(s)`.
Development of charges on the species produced suggests us to rewrite the above reaction in the following manner
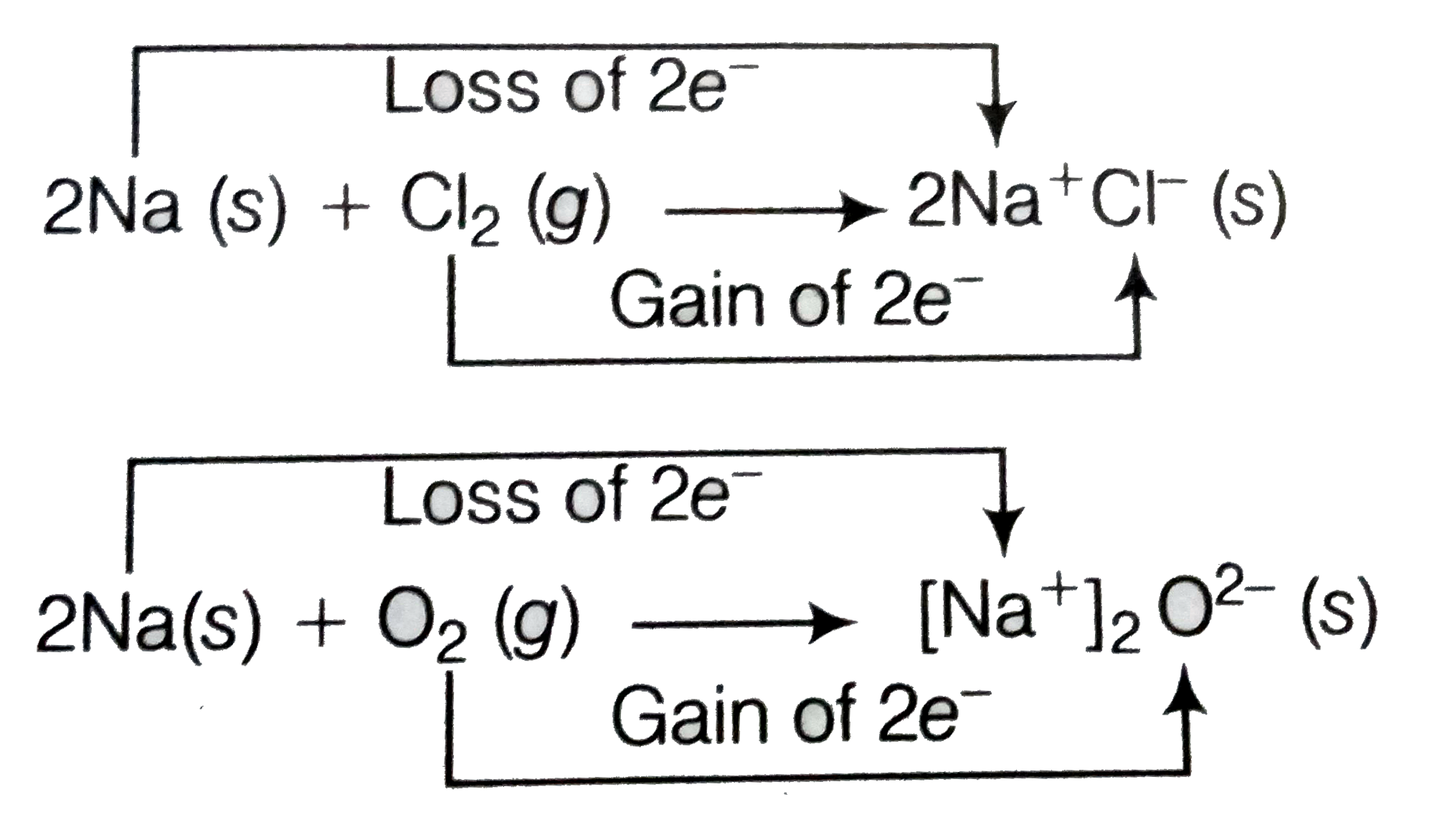
For convenience, each of the above processes can be considered as two separate steps, one involving the loss of electrons and other the gain of electrons. As as illustration, we may further elaborate one of these, say, the formation of sodium chloride
`2Na(s)to2Na^(+)(g)+2e^(-)`
`Cl_(2)+2e^(-)to2Cl^(-)(g)`
Each of the above steps is called a half reaction, which explicitly shows, involvement of electrons. Sum of the half reactions gives the overall reaction:
`2Na(s)+Cl_(2)(g)to2Na^(+)Cl^(-)(s)or 2NaCl(s)`
The given reactions suggest that half reactions that involved loss of electrons are oxidation reactions. Similarly, the half reactions that involve gain of elecrons are called reduction reactions.
It may not be out of context to mention here that the new way of defining oxidation and reduction has been achieved only by establishing a correlation between the behaviour of species as per the classical idea and their interplay in electron-transfer change.
In the given reactions, sodium, which is oxidised, acts as a reducing agent because it donates electron to each of the elements interacting with it and thus helps in reducing them.Chlorine and oxygen are reduced and act as oxidising agents because these accept eelctrons from sodium.
To summarise, we may mention that
Oxidation Loss of electron(s) by any species
Reduction Gain of electron(s) by any species.
Oxidising agent Acceptor of electron(s).
Reducing agent Donor of electron(s).
