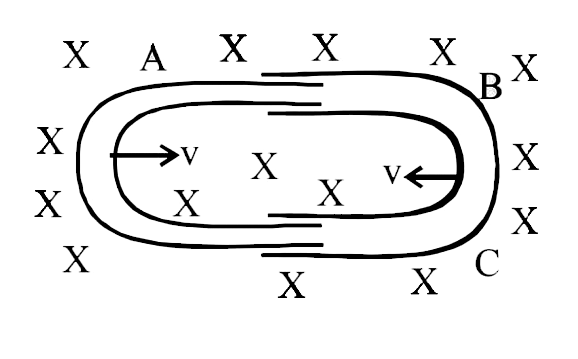
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercis-3 PART 3|16 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE|Exercise A.l.P|19 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercis-3 PART 1|18 VideosELECTRODYNAMICS
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced level problems|31 VideosELECTROSTATICS
RESONANCE|Exercise HLP|39 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Exercis-3 PART 2
- One conducting U tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, mai...
Text Solution
|
- A coil of inductance 300mh and resistance 2Omega is connected to a sou...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor (L = 100 mH), a resistor (R = 100 (Omega)) and a battery (...
Text Solution
|
- Two coaxial solenoids are made by winding thin insulated wire over a p...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor of inductance L = 400 mH and resistors of resistance R(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular loop has a sliding connector PQ of length l and resistan...
Text Solution
|
- A fully charged capacitor C with initial charge q(0) is connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- A boat is moving due east in a region where the earth's magnetic field...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal straight wire 20 m long extending from east to west falli...
Text Solution
|
- A coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 'l' is tied to a string of length 2l and made...
Text Solution
|
- A circular loop of radius 0.3 cm lies parallel to amuch bigger circula...
Text Solution
|
- In an LCR circuit as shown below both switches are open initially. Now...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown here, the point 'C' is kept connected to point 'A...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor (L =0.03 H) and a resistor (R = 0.15k(Omega)) are connecte...
Text Solution
|
- An LCR curcuit is equivalent to a damped pendulum. In an LCR circuit t...
Text Solution
|