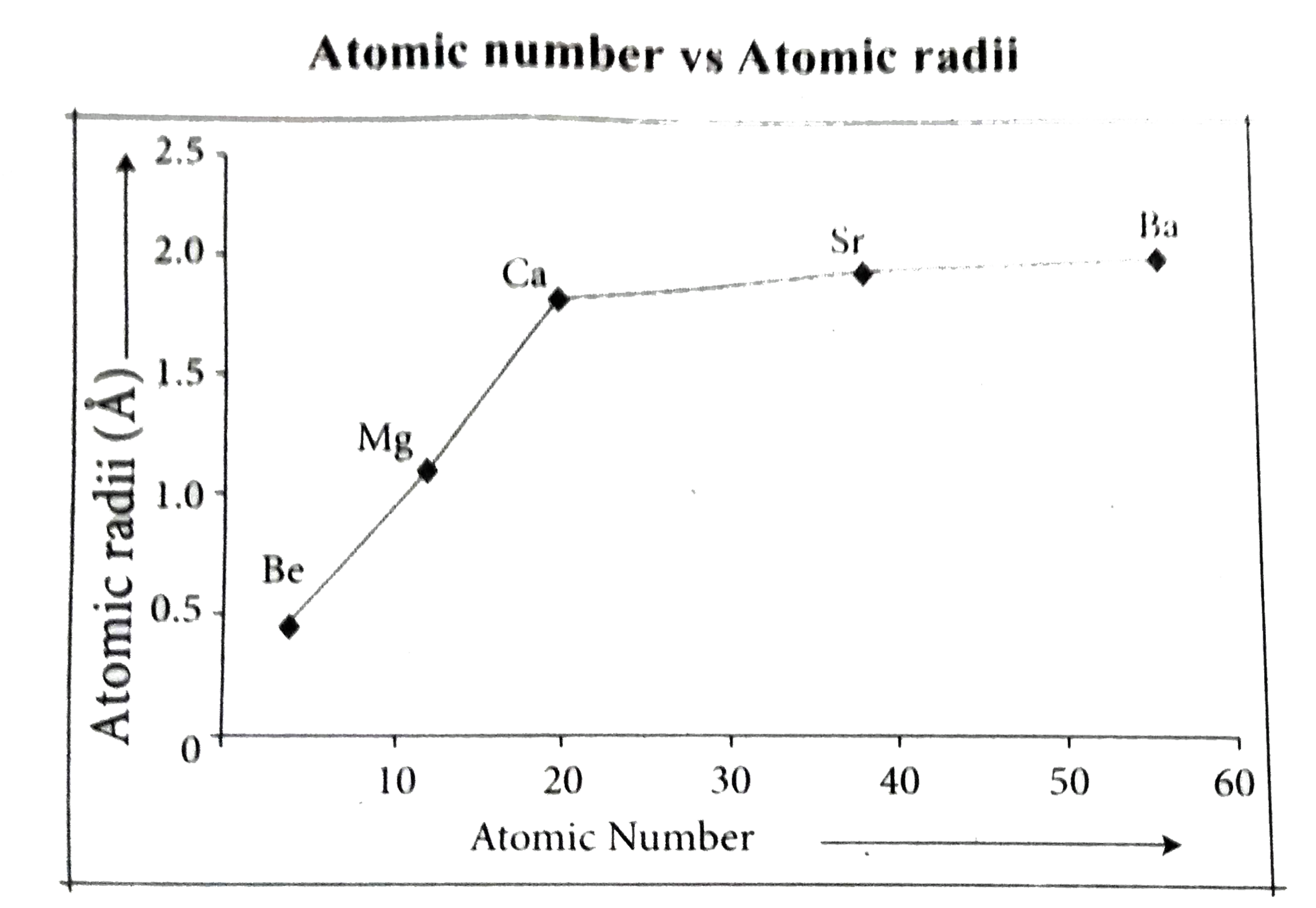
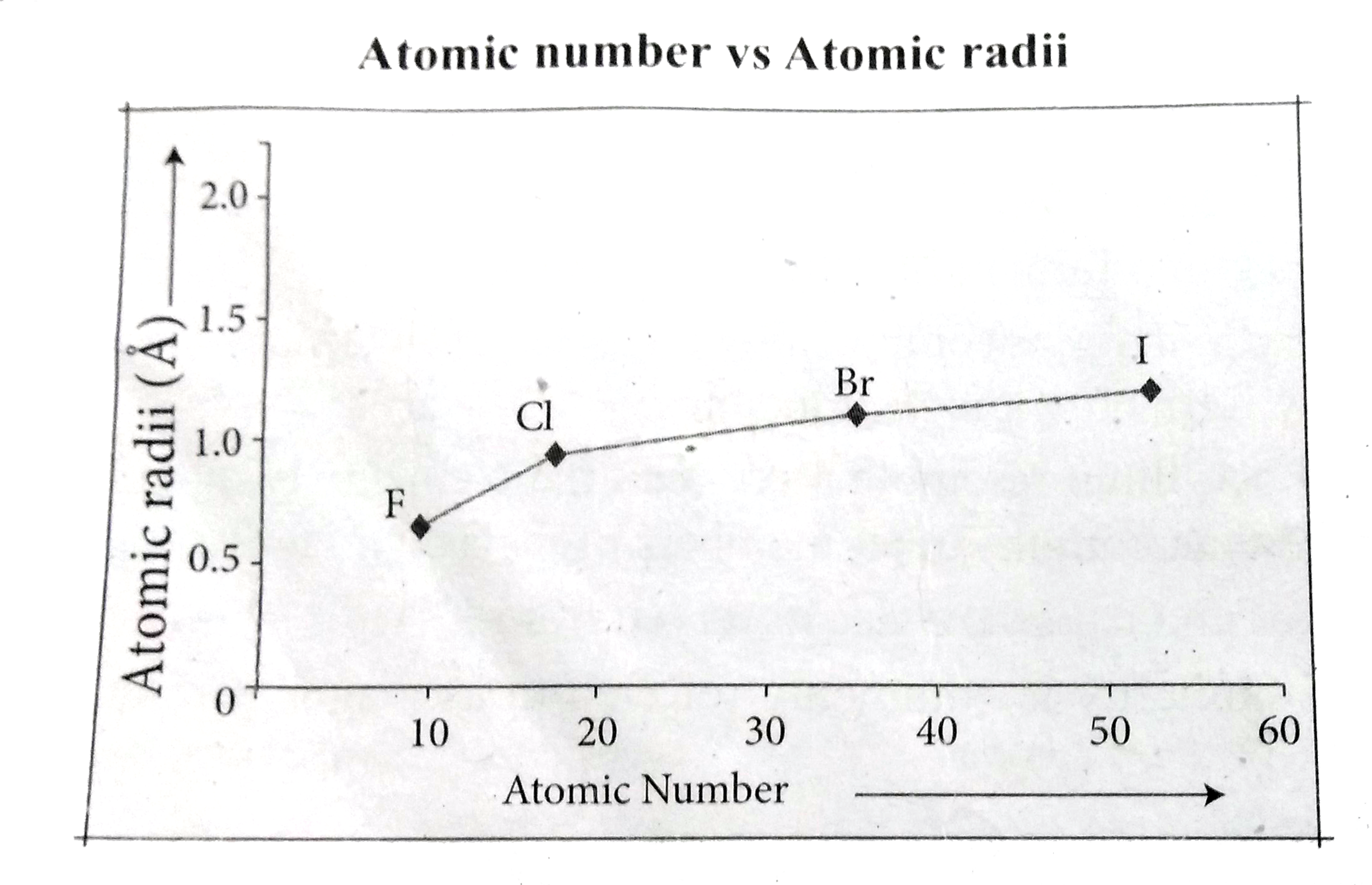
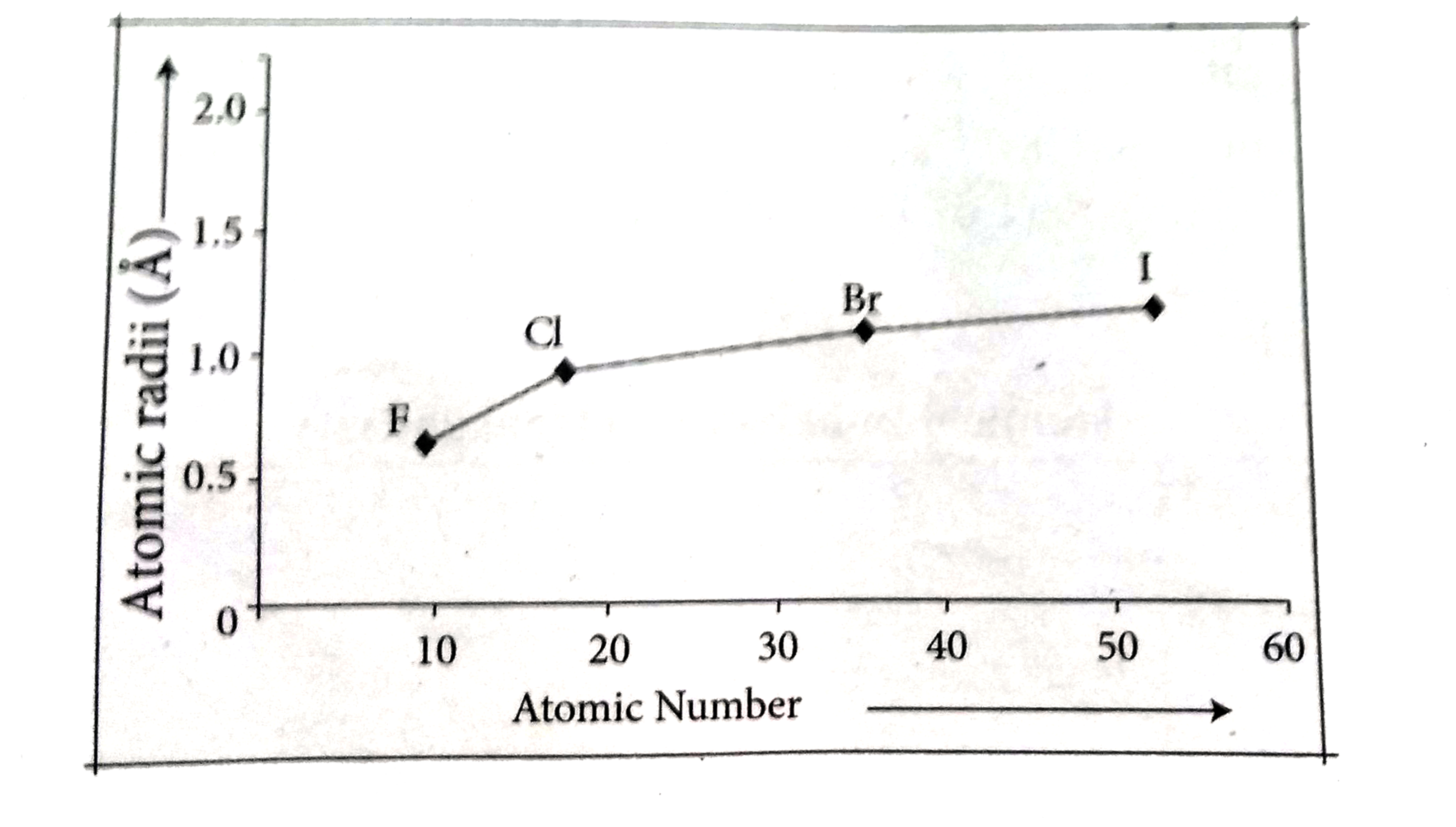
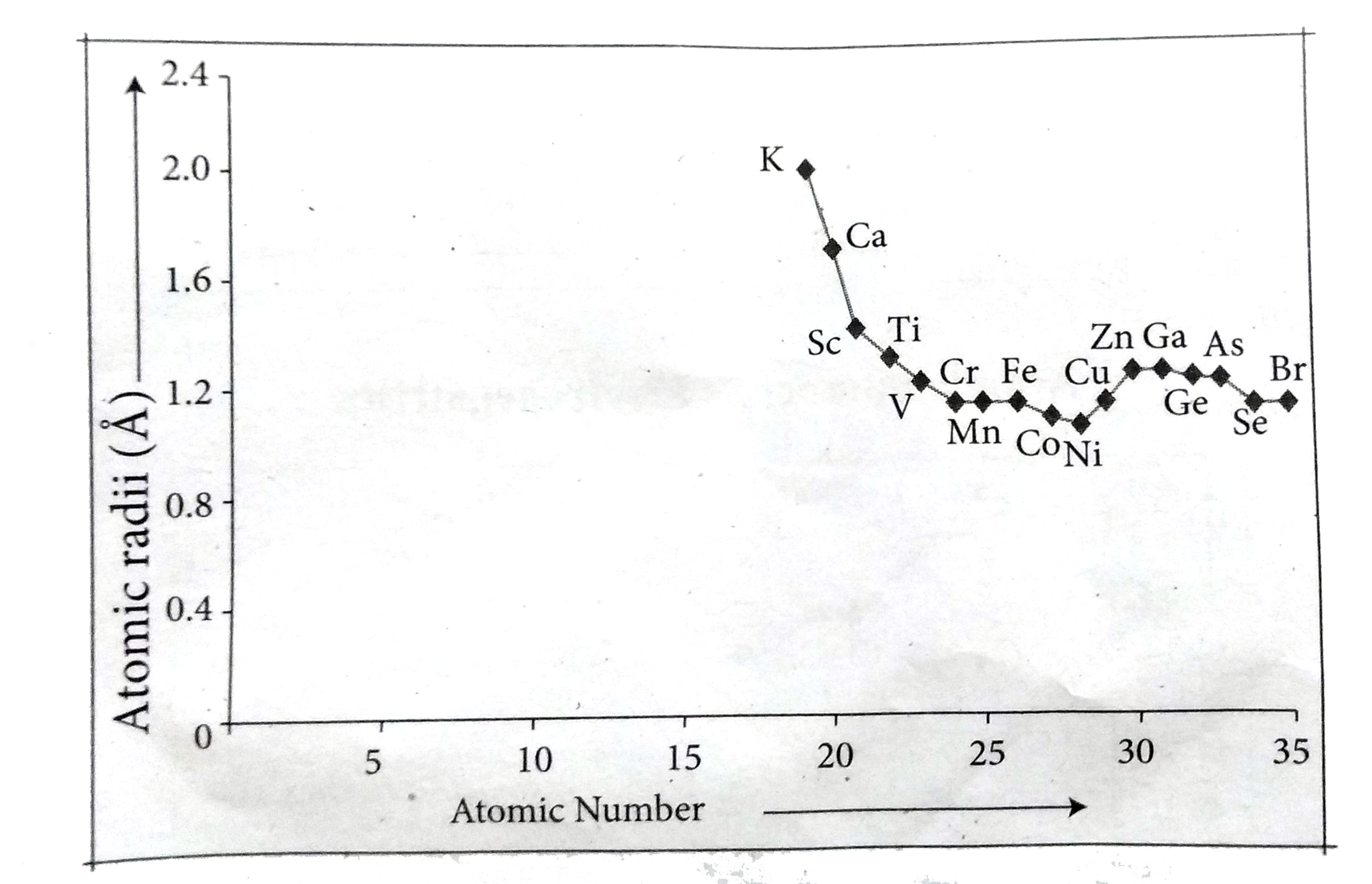
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Activity 3.2|1 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Higher Order Thinking skills (HOTS) Questions|10 VideosHYDROGEN
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions Solved 5-Mark Questions|10 VideosPHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED (NUMERICAL PROBLEMS)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems