Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CBSE MODEL PAPER-SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (CHEMISTRY )-SECTION C
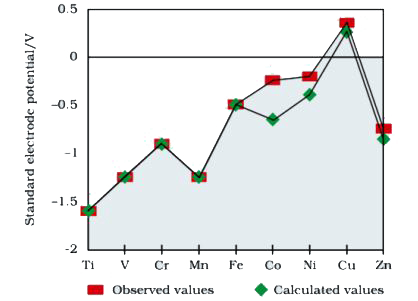
- Observed and calculated values for the standard electrode potentials o...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following in increasing order of property specified: i. ...
Text Solution
|
- i. Give a chemical test to distinguish between N-methylethanamine and ...
Text Solution
|
- A metal crystallizes into two cubic phases, face-centred cubic and bod...
Text Solution
|
- Three amino acids are given below: Alanine CH(3)CH(COOH)(NH(2)) Aspart...
Text Solution
|
- i. Arrange the following in decreasing order of bond dissociation enth...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Answer the following questions: a) Arrange the following in the...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound ‘A’ C(8)H(6) on treatment with dilute H(2)SO(4) co...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Write the reaction for cross aldol condensation of acetone and eth...
Text Solution
|
- (i) State Kohlrausch law. (ii) Calculate the emf of the following c...
Text Solution
|
- On the basis of Eo values identify which amongst the following is the ...
Text Solution
|