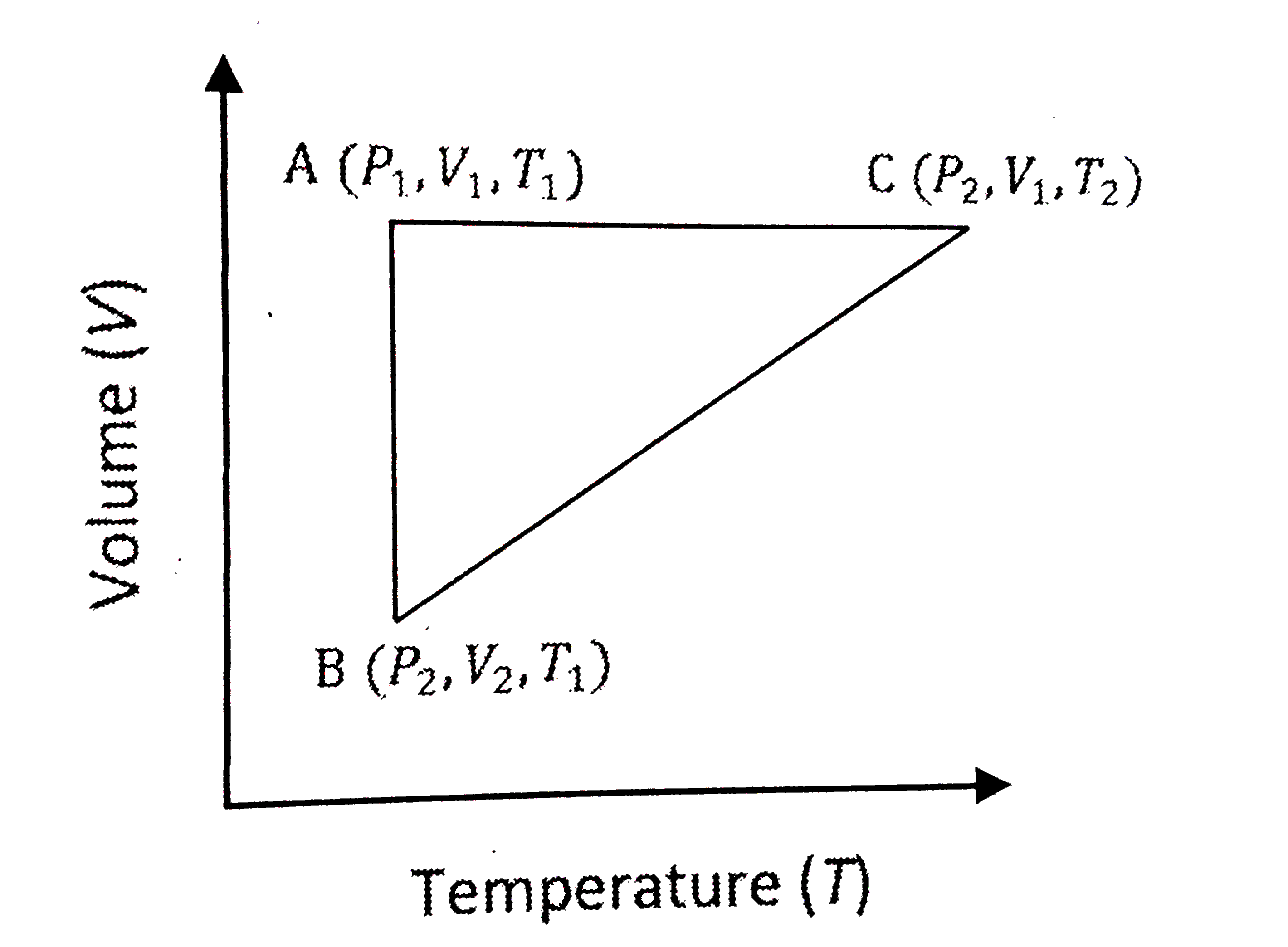
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS AND THERMOCHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS |Exercise JEE section (JEE (Advanced) 2018) Numeric answer type questions|2 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS AND THERMOCHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS |Exercise JEE section (Matrix Match type questions)|4 VideosSOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
ERRORLESS |Exercise JEE Section (Matrix Match type questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems