Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-SECTION - C
- (a) State Biot - Savart law and ecpress it in the vector form. (b...
Text Solution
|
- Define electric flux and write its SI unit . The electric field compon...
Text Solution
|
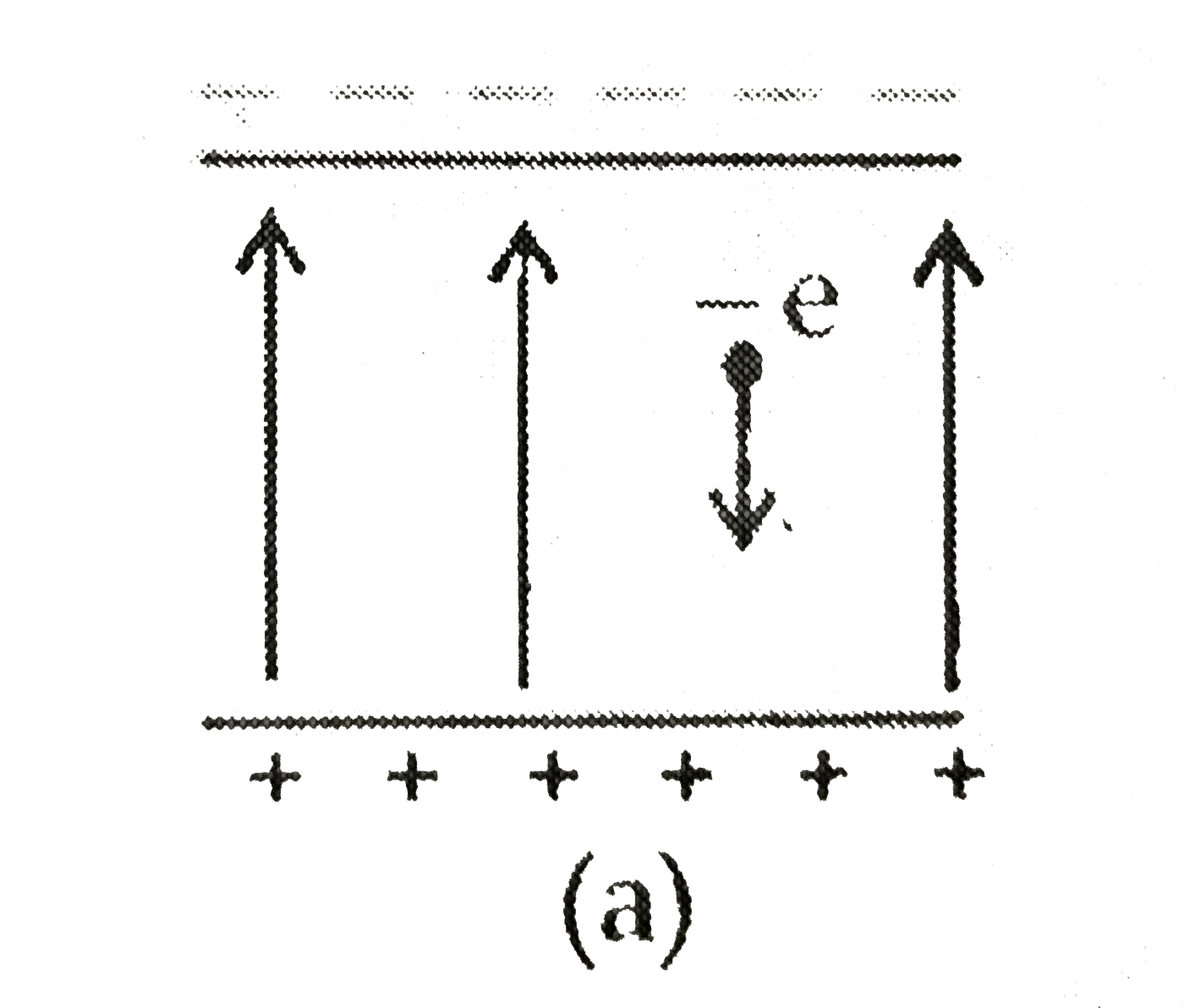
- An electron falls through a distance of 1.5 cm in a uniform electric f...
Text Solution
|
- Using Kirchhoff ' s rules , calculate the potential difference between...
Text Solution
|
- Define SI unit of current in terms of the force between two parallel c...
Text Solution
|
- (a) With the help pf a ray diagram , show how a concave mirror is use...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of emfs epsilon(1)and epsilon(2) and internal resistances ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Write two points to distinguish between interference and diffracti...
Text Solution
|
- (a) When an unpolarized light of intensity I(0) is passed through a p...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write the truth table for the combination of the gates shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- When a given photosensitive material is irradiated with light of frequ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw graph showing the variation of current versus voltage in an e...
Text Solution
|
- For the circuit would the balancing length increase, decrease or remai...
Text Solution
|
- State the underlying princeiple of mater bridge. Draw the circuit diag...
Text Solution
|
- A proton, a deuteron and an alpha particle, are accelerated through th...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Briefly explain how a galvanometer is converted into an ammeter. ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Briefly explain how a galvanometer is converted into a voltmeter. ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows arectangular conducting frame MNOP of resistance R pl...
Text Solution
|
- Draw aray diagram to show the image formation of a distant object by a...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Plot a graph for angle of deviation as a function of angle of inci...
Text Solution
|