Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES|58 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise CASE BASED/SOURCE-BASED INTEGRATED QUESTION|15 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS - I|21 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION D)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-COORDINATION COMPOUNDS-SELF ASSESSMENT TEST
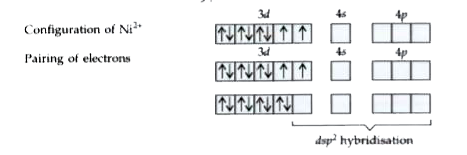
- Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)(4)]^(2-) ion ...
Text Solution
|
- Which type of shapes are uncommon in coordination compounds ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not a double salt?
Text Solution
|
- What is the coordination number of metal in the complex ion [Fe(C(2)O(...
Text Solution
|
- Which type of isomerism is shown by [Cr(H(2)O)(6)]Cl(3) and [Cr(H(2)O)...
Text Solution
|
- Chlorophyll which is responsible for photosynthesis is a complex compo...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : Valence bond theory does not give quantitative interpr...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : Coordination isomerism arises in a coordination compou...
Text Solution
|