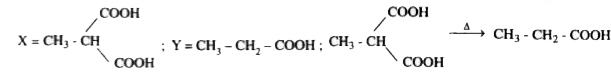A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (Linked Comprehension Type Questions)|7 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (Matching Type Questions)|2 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-4 (Single Answer questions)|6 VideosCARBOHYDRATES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Practice Sheet-5|30 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND DERIVATIVES
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise CONVERSIONS|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-CARBOXYLIC ACIDS -PRACTICE SHEET-4 (More than one correct answer questions)
- A carboxylic acid (X) of unknown structure was found to contain only C...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is given correctly inter pretested .
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reactions is/are correctly represented
Text Solution
|
- Acetophenone overset(NaNO2//HCl)to A underset(Delta)overset(AC2O)to B ...
Text Solution
|
- H2 C=C=O+ CH2 N2 overset(-78^@ C)to Product . Correct statements abo...
Text Solution
|
- Correct option regarding above reaction is
Text Solution
|
- CH2 = C=O to underset("(dilketene)")X Correct statement is
Text Solution
|