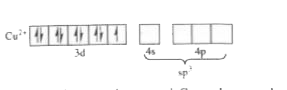
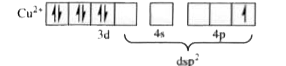
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LEVEL-II EXERCISE-III (Match the following questions)|13 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LEVEL-II EXERCISE-IV (Integer answer type Questions)|8 VideosCO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise LEVEL-II LECTURE SHEET EXERCISE-II (Linked Comprehension type questions ) Passage-V|3 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET - 2 (PRACTICE SHEET -2 (INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS))|7 VideosCOMPLEX COMPOUNDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE EXERCISE|45 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems