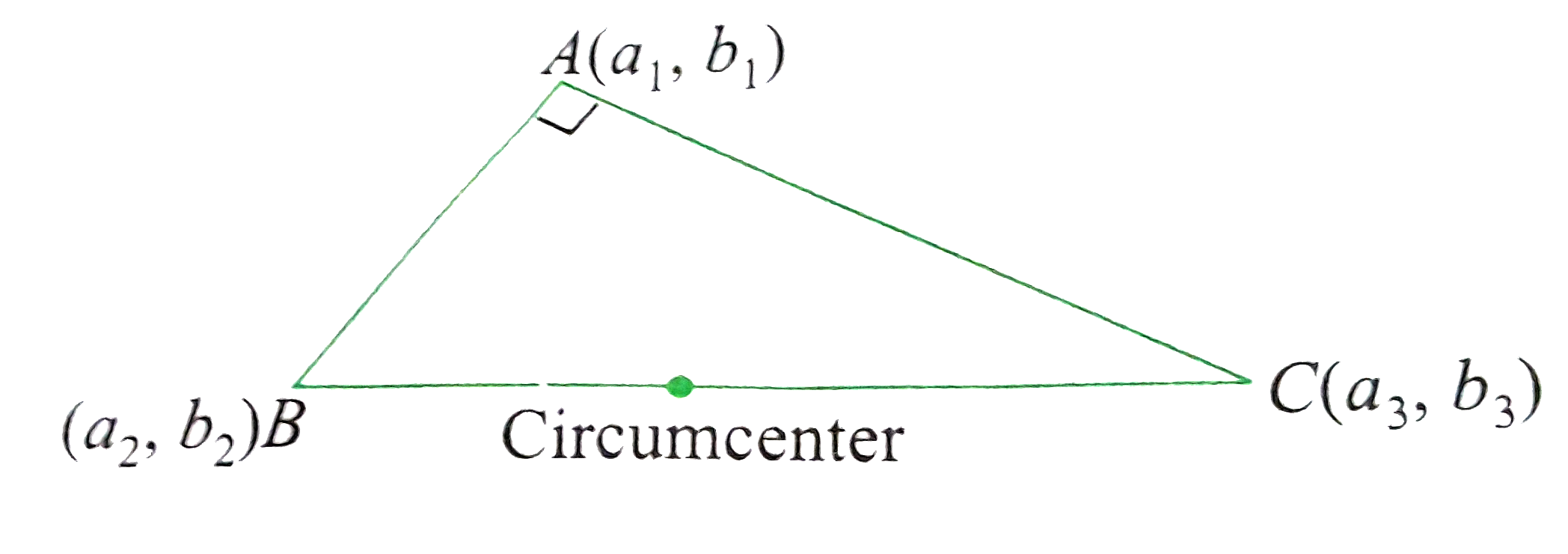
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
COORDINATE SYSYEM
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration1.48|1 VideosCOORDINATE SYSYEM
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration1.49|1 VideosCOORDINATE SYSYEM
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration1.46|1 VideosCOORDINATE SYSTEM
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Answers Type|2 VideosCROSS PRODUCTS
CENGAGE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP 2.2|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems