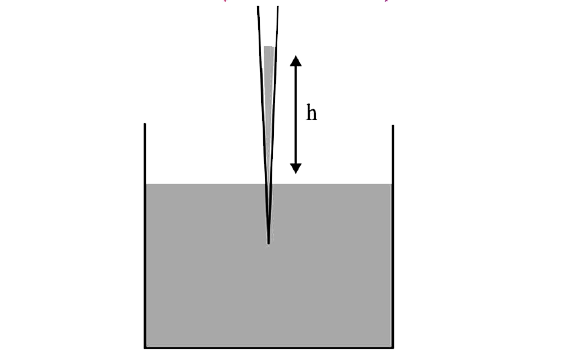
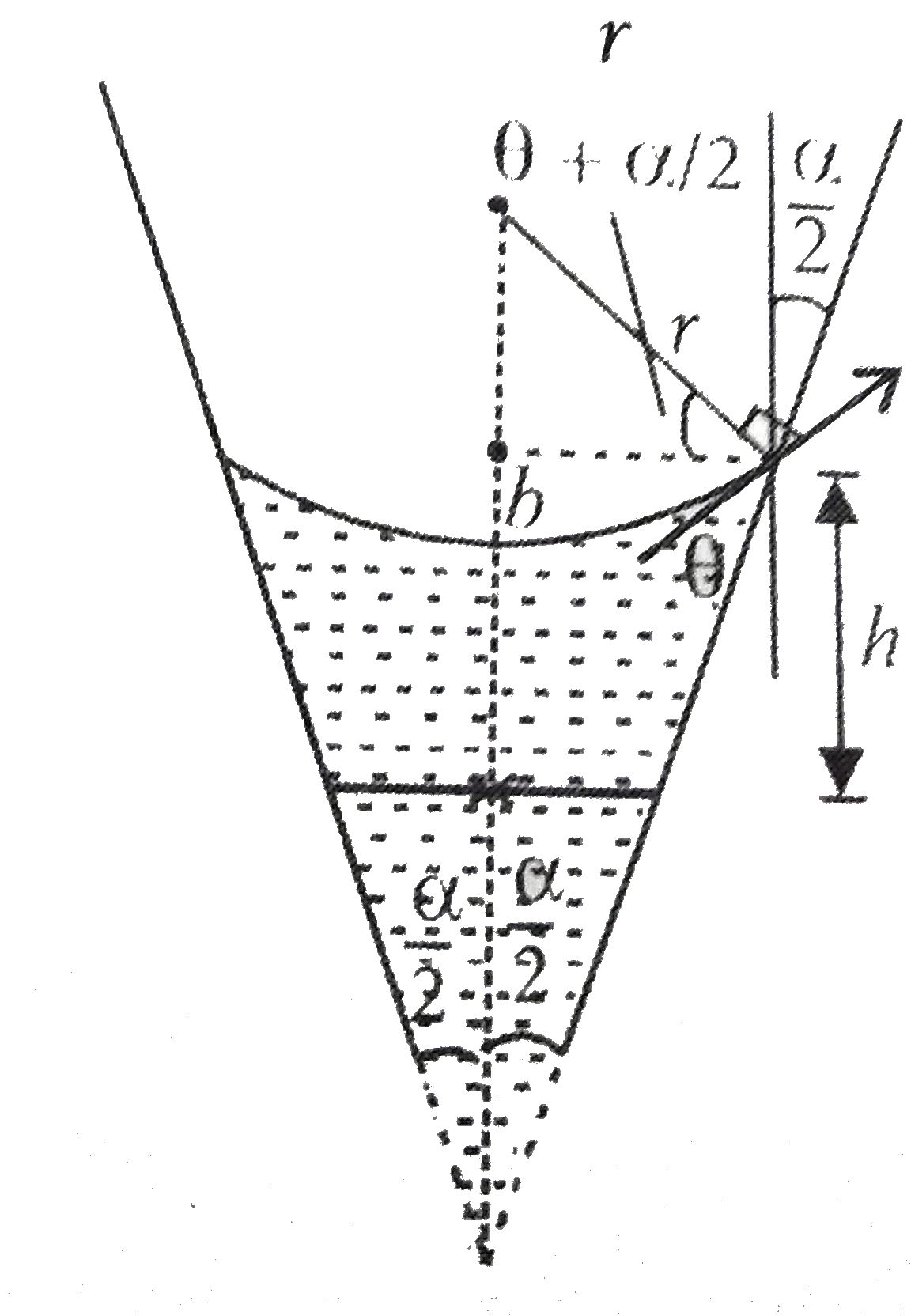
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Exemplar Problems|5 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion and reason|15 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|5 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS-Higher Order Thinking Skills
- A glass capillary tube is of the shape of a truncated cone with an ape...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of length L and mass M having cross-sectional area ...
Text Solution
|
- A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still...
Text Solution
|
- A bubble having surface tension T and radius R is formed on a ring of ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains two immiscible liquids of density rho(1)=1000 kg//m^...
Text Solution
|
- A glass tube int the form of an equilateral triangle of uniform cross-...
Text Solution
|
- Two soap bubbles A and B are kept in a closed chamber where the air is...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical vessel of height 500mm has an orifice (small hole) at it...
Text Solution
|