A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
METALLURGY
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise Level 3 (Passive 3)|6 VideosMETALLURGY
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise Level 3 (Passive 4)|4 VideosMETALLURGY
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise Level 3 (Passive 1)|8 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|14 Videosp-BLOCK ELEMENTS
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS|35 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VK JAISWAL ENGLISH-METALLURGY-Level 3 (Passive 2)
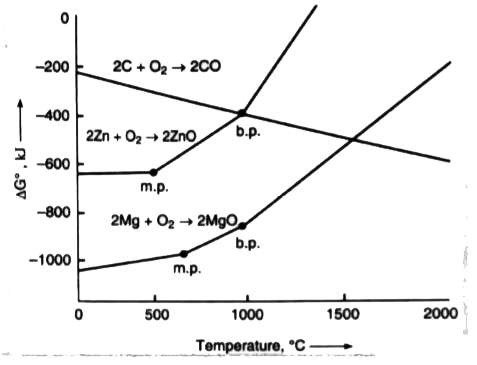
- The ellingham diagram for zinc, magnesium and carbon coverting into co...
Text Solution
|
- The ellingham diagram for zinc, magnesium and carbon coverting into co...
Text Solution
|
- The ellingham diagram for zinc, magnesium and carbon coverting into co...
Text Solution
|
- The ellingham diagram for zinc, magnesium and carbon coverting into co...
Text Solution
|
- The ellingham diagram for zinc, magnesium and carbon coverting into co...
Text Solution
|
- The ellingham diagram for zinc, magnesium and carbon coverting into co...
Text Solution
|