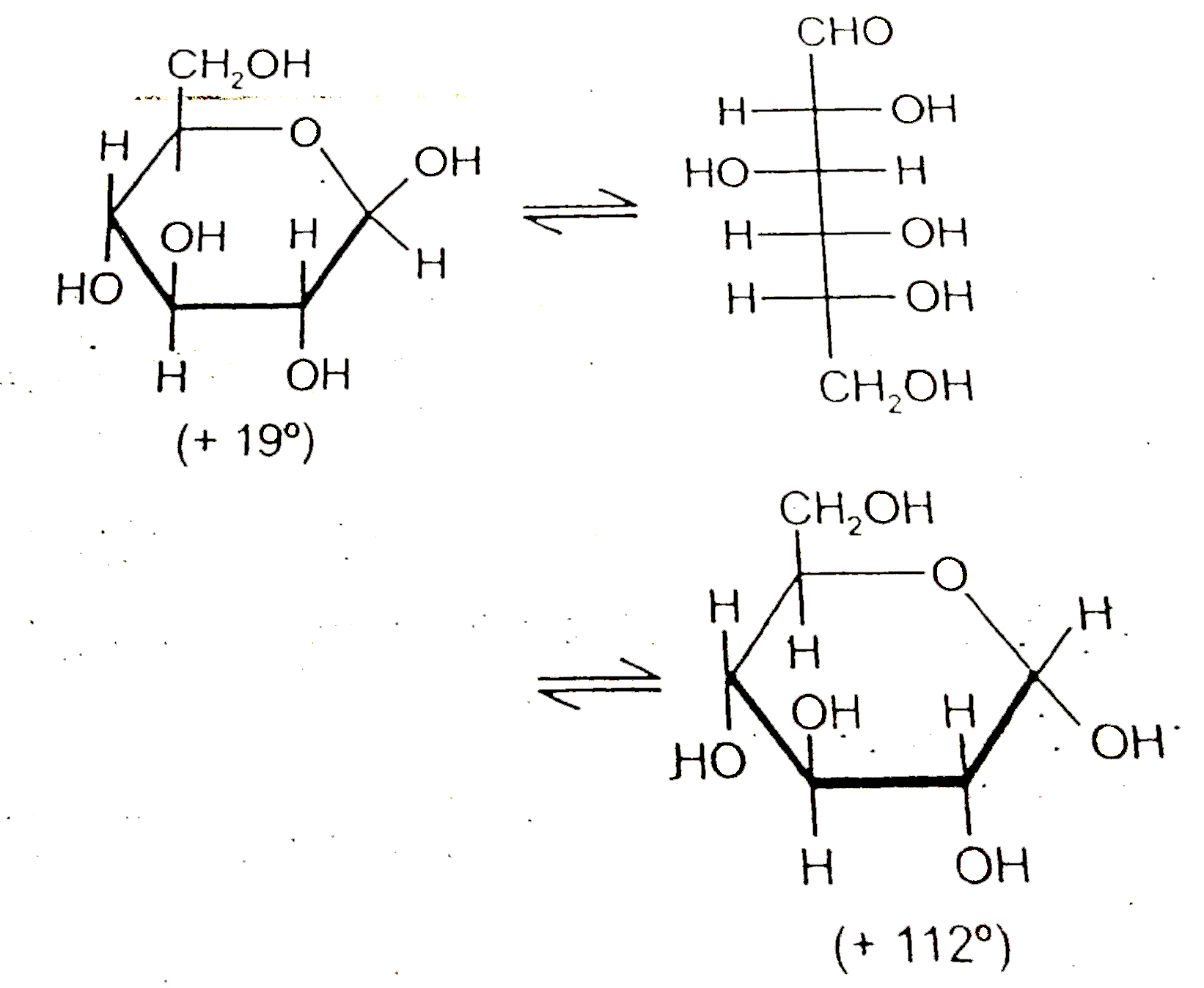
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BIOMOLECULES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Section-E (Assertion-Reason Type Questions )|5 VideosBIOMOLECULES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Section-E (Matrix match Type Questions )|6 VideosBIOMOLECULES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Section-C (Objective Type Questions (More than one option is correct))|10 VideosAMINES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section -J (Aakash Challengers Questions)|9 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section J (Aakash Challengers Questions)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-BIOMOLECULES-Section-D (Comprehension Questions )
- When either form of D-Glucose is dissolved In water, the solution grad...
Text Solution
|
- When either form of D-Glucose is dissolved In water, the solution grad...
Text Solution
|
- When either form of D-Glucose is dissolved In water, the solution grad...
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acids containing an amino group (-NH(2)) as a substituent a...
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acids containing an amino group (-NH(2)) as a substituent a...
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic acids containing an amino group (-NH(2)) as a substituent a...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes ahd ketones are converted to acetals by treatment with an al...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones are converted to acetals by treatment with an al...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes ahd ketones are converted to acetals by treatment with an al...
Text Solution
|