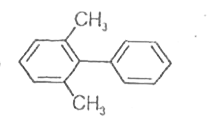
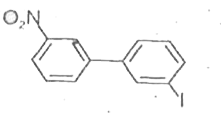
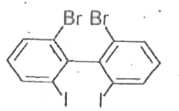
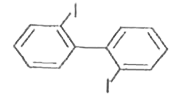
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT SECTION -D|15 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT SECTION - B|25 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|33 VideosHYDROCARBONS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment(Section - C) (Previous Years Questions)|60 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES -ASSIGNMENT SECTION - C
- Identify A and predict the type of reactions
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reaction : CH(3)CH(2)CH(2)Br+NaCNrarrCH(3)CH(2)CH(2)CN+...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following biphenyls is optically active?
Text Solution
|
- Two possible stereostructures of CH(3)CHOH.COOH, which are optically a...
Text Solution
|
- In an S(N)1reaction on chiral centres, there is
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following compounds , the C - Cl bond ioniosation shal...
Text Solution
|
- What products are formed when the following compounds are treated with...
Text Solution
|
- CH2=CH2 + Br = Product , what is product?
Text Solution
|
- In the replacement reaction rarrC-I+MF rarr rarr C-F+MI The react...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution r...
Text Solution
|
- Condiser the reactions, (i) (CH(3))(2)CH-CH(2)Broverset(C(2)H(5)OH)r...
Text Solution
|
- The correct order of increasing reactivity of C-X bond towards nucleop...
Text Solution
|
- Which one is most reactive towards S(N)1 reactions ?
Text Solution
|
- In the following reaction C(6)H(5)CH(2)Br underset(2.H(3)O)overset(1...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reactions is an example of nucleophilic substit...
Text Solution
|
- H(3)C-underset(CH(3))underset("| ")"CH"-CH-=CH(2)+HBrrarr(X) Here (...
Text Solution
|
- In a S(N^(2)) substitution reaction of the type R-Br+Cl^(-)overset("...
Text Solution
|
- If there is no rotation of plane polarized light by a compound in a sp...
Text Solution
|
- For the following: (a) I^(-) (b) Cl^(-) (c) Br^(-) The ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively...
Text Solution
|