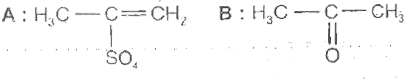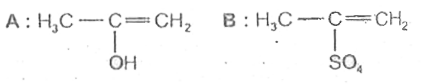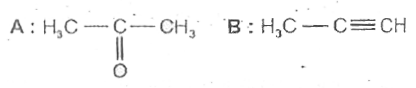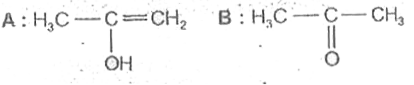A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment(Section - B) (Obejctive type question)|5 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT SECTION -D|15 VideosHYDROGEN
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION - D) (Assertion-Reason Type question)|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-HYDROCARBONS-Assignment(Section - C) (Previous Years Questions)
- H(3)C-C-=CH overset(H(2)O,H(4)SO(4))underset(HgSO(4))to underset(A)("i...
Text Solution
|
- Which one is the correct order of acidity ?
Text Solution
|
- With respect to the conformers of ethane, which of the following state...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following can be used as the halide component for Friedel...
Text Solution
|
- The product P is
Text Solution
|
- Which is expected to react most readily with bromine
Text Solution
|
- In the reactions HC-=CHoverset((1)NaNH(2) // liq. NH(3))underset((2)CH...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the nitration of benzene using mixed conc. H(2)SO(4) and HNO(...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction with HCl, an alkene reacts in accordance with Markowni...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of C(6) H(5) CH=CHCH(3) with HBr produces :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following organic compounds has same hybridisation as its...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reagents will be able to distinguish between 1-...
Text Solution
|
- Liquid hydrocarbon is converted to a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons b...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of toluene with CI(2) in presence of FeCI(3) gives X and ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following the most stable conformation of n-butane is
Text Solution
|
- Benzene reacts with CH(3)Cl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl(3) to ...
Text Solution
|
- Nitrobenzene can be prepared from benzene by using a mixture of conc....
Text Solution
|
- How many stereoisomers does this molecule have ? CH(3)CH=CHCH(2)CHBr...
Text Solution
|
- The order decreasing reactivity towards an electrophilic reagent, for ...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the product C obtained in the following reaction of butyne-1: ...
Text Solution
|