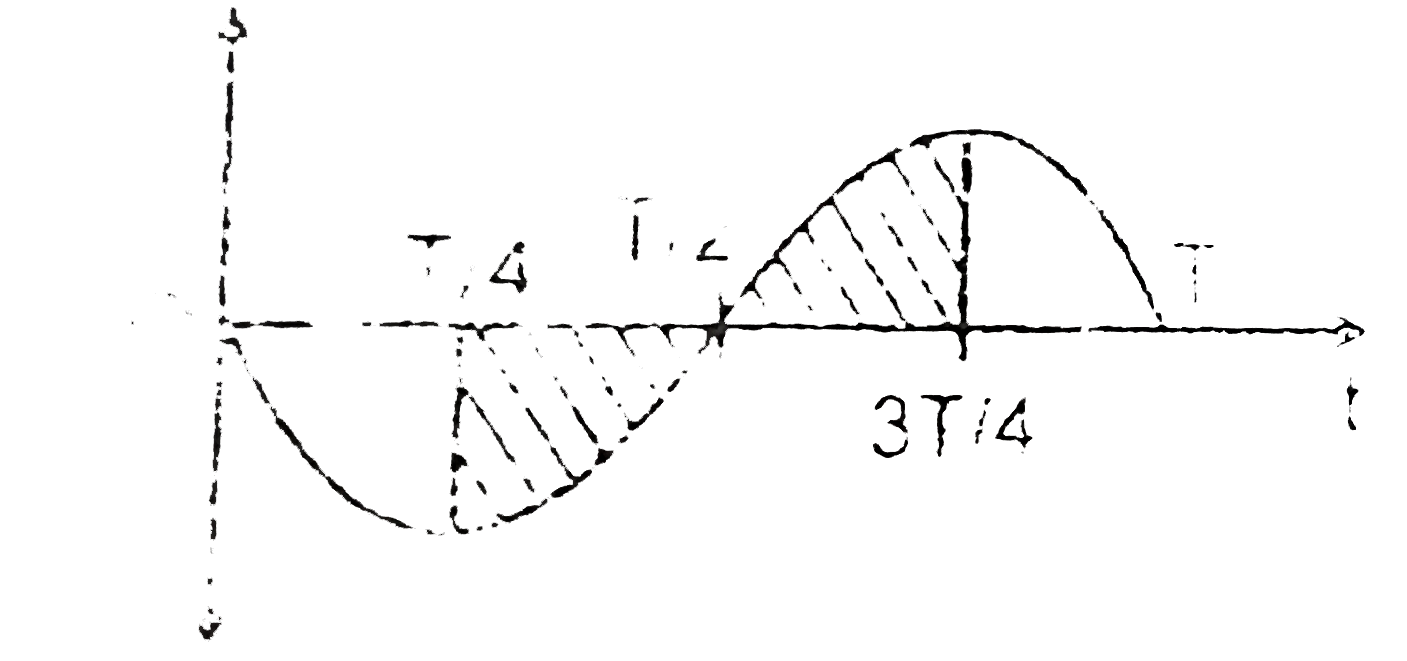
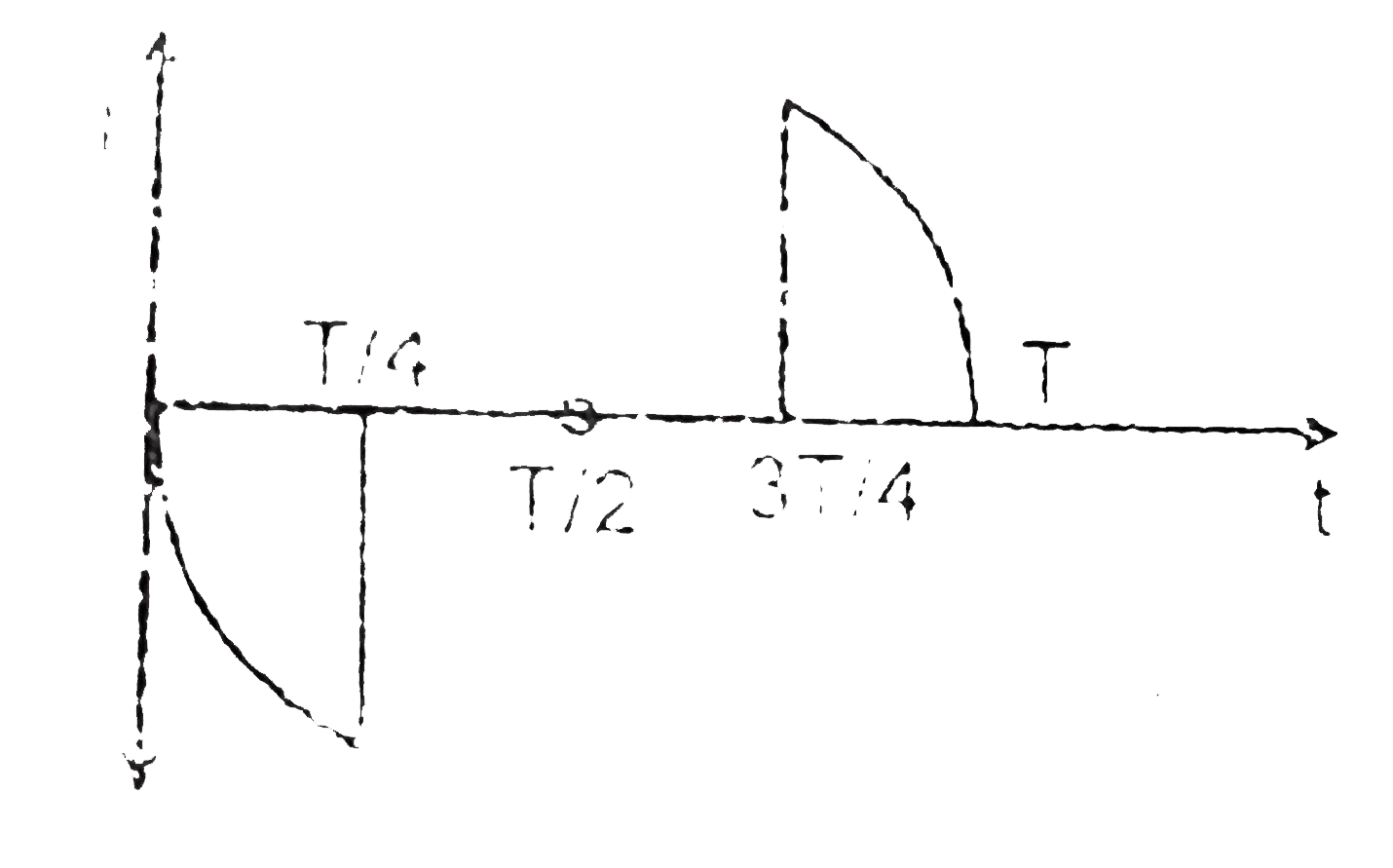
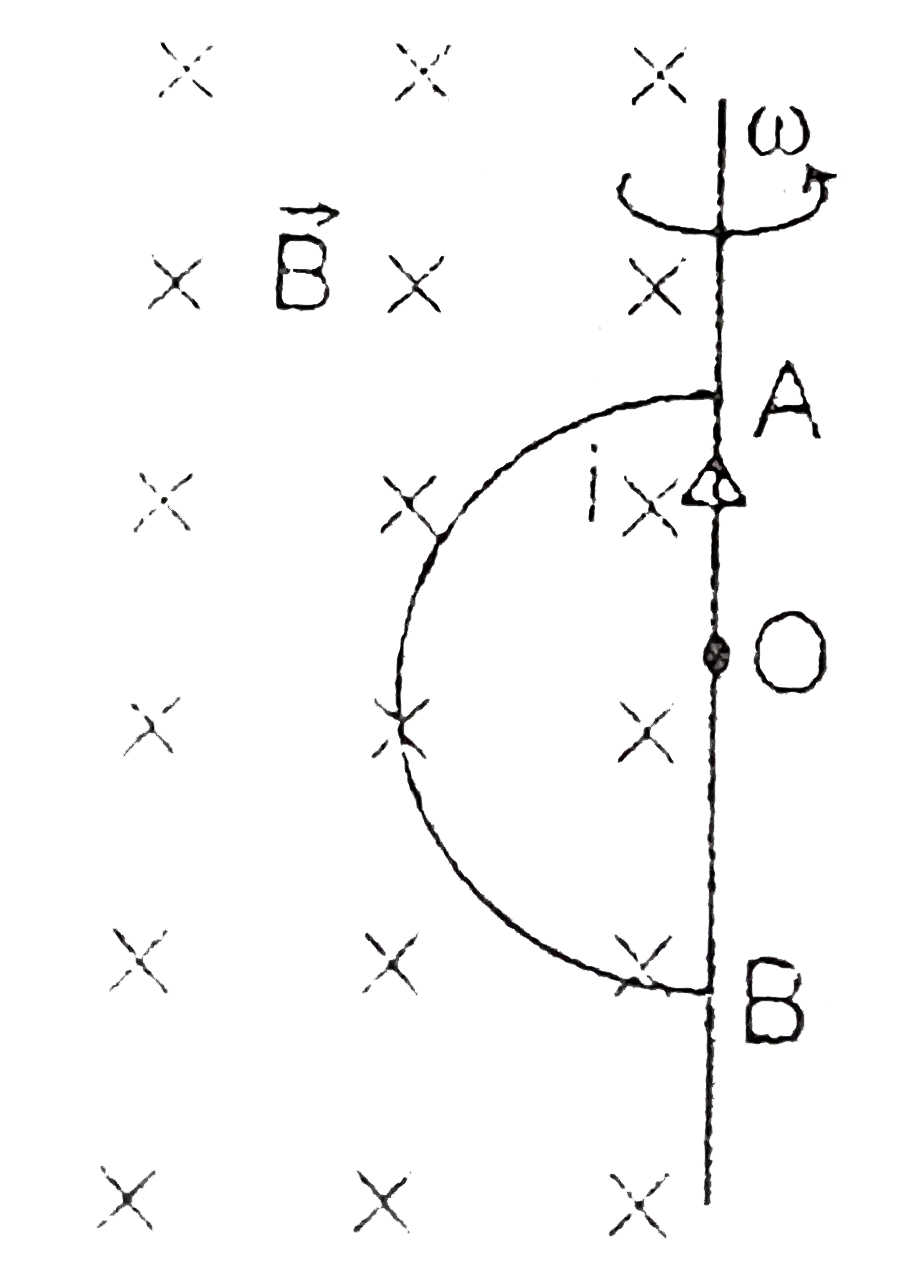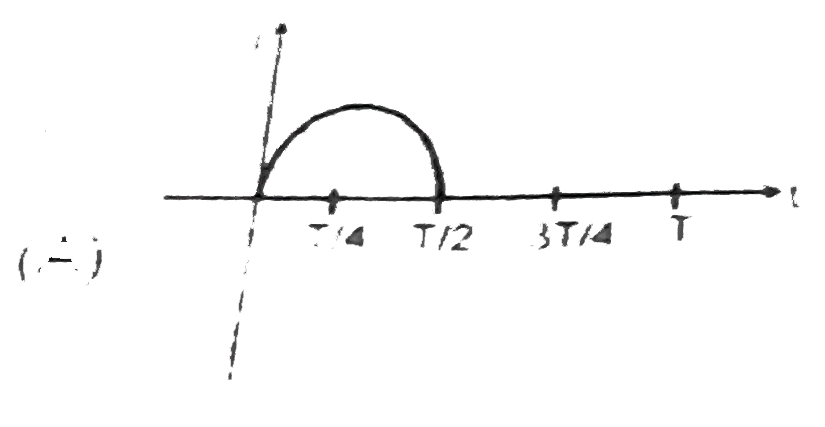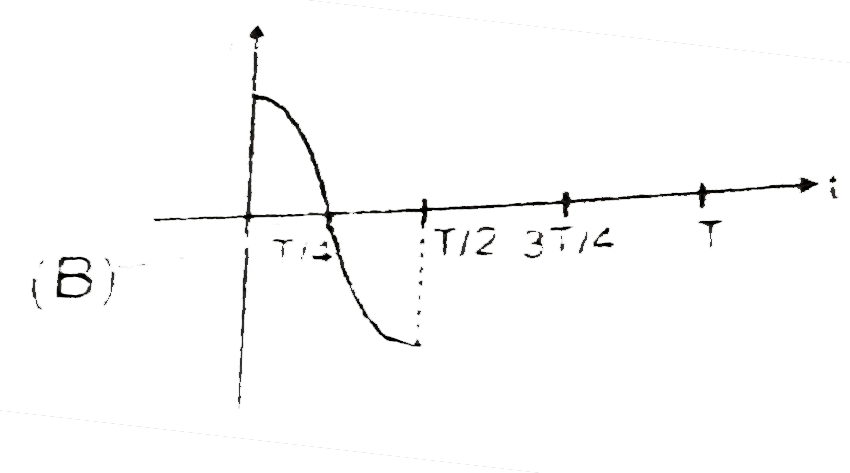A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.63|9 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.64|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise DPP No.61|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|19 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.62
- A semicircular loop of radius R is rotated about its straight edge whi...
Text Solution
|
- An aeroplane is flying in vertical plane at an angle of 30^(@) with t...
Text Solution
|
- A gun of mass M fires a bullet of mass m with a horizontal speed V. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is free to rotate about its fixe...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylindrical pulley of mass m and radius R = 10 cm is hinged ab...
Text Solution
|
- S(2) is a fixed rough sphere and S(1) is a uniform solid sphere S(1) i...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls having masses m and 2m are fasrtened to two light strings of...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls having masses m and 2m are fastened to two light strings of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls having masses m and 2m are fasrtened to two light strings of...
Text Solution
|