Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST 8 (2020)-PHYSICS (SECTION 2)
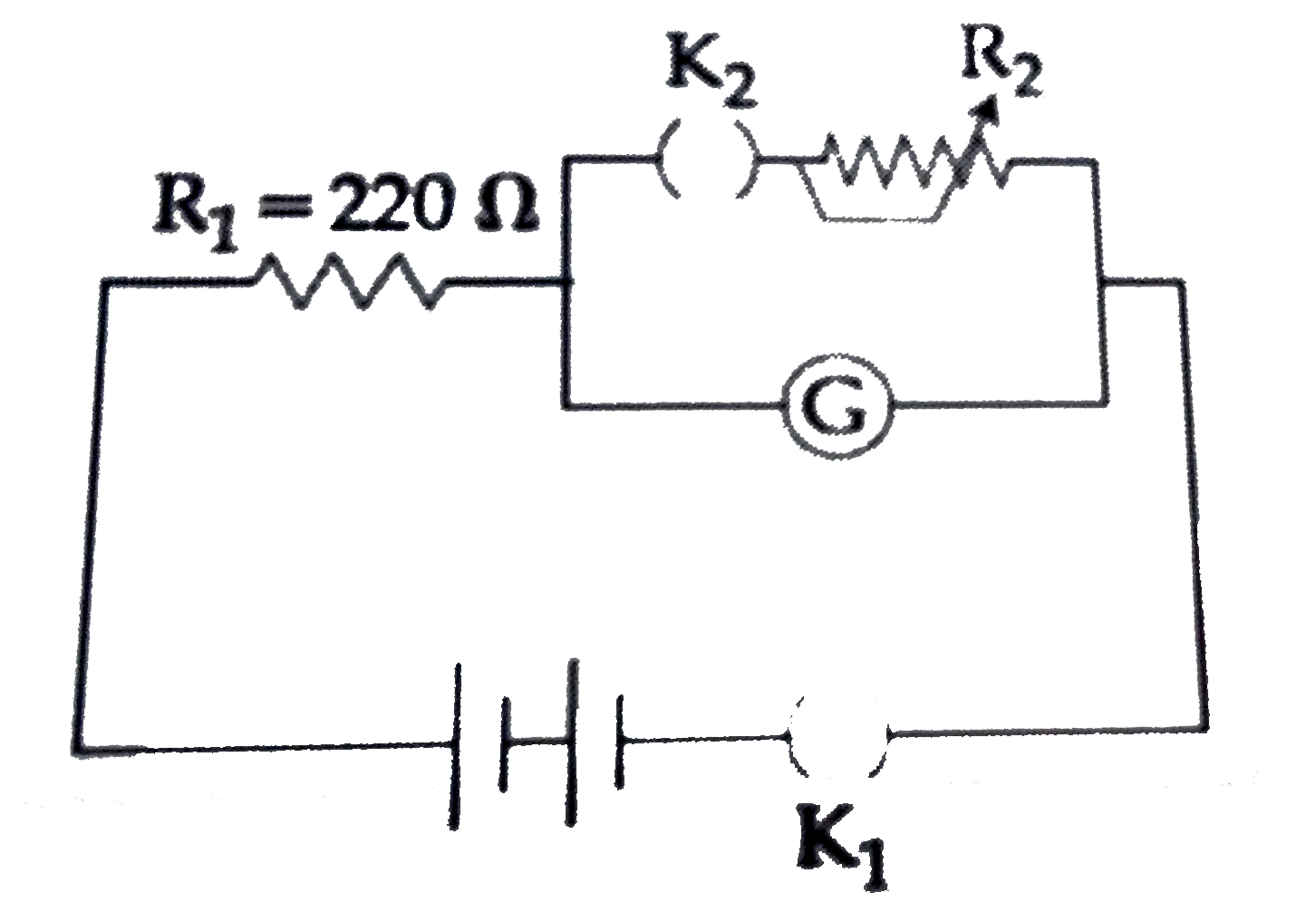
- The galvanometer deflection , when key K(1) is closed but K(2) is o...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown , after the switch 's' is turned from postion ...
Text Solution
|
- in the figure shown , a circuit contains two identical resistors wit...
Text Solution
|
- for the given cyclic process CAB as shown for a gas , the work don...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light S, placed at a distance L in front of the cen...
Text Solution
|