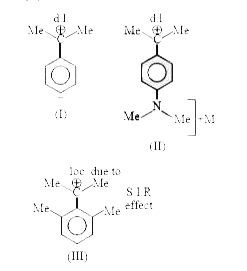
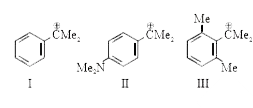A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KVPY PREVIOUS YEAR-QUESTION PAPER 2020-PART-I (CHEMISTRY )
- The Stability of Follow the order
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the biodegradable polymer is :
Text Solution
|
- Among the following, the compounds which can be reduced with for...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound that is commonly used for sanitizing surfaces is :
Text Solution
|
- The rates of reaction of NaOH with follow the order :-
Text Solution
|
- The most suitable reagent for the conversion of 2-phenylpropanamide in...
Text Solution
|
- The compound X in the following reaction scheme :
Text Solution
|
- A nucleus X captures a beta particle and then emits a neutron and gamm...
Text Solution
|
- The boiling point (in ""^@C) of 0.1 molal aqueous solution of CuSO4.5H...
Text Solution
|
- A weak acid is titrated with a weak base. Consider the following statm...
Text Solution
|
- Products are favored in a chemical reaction taking place at a constan...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of toluene and benzene forms a nearly ideal solution. Assume...
Text Solution
|
- Upon dipping a copper rod, the aqueous solution of the salt that can ...
Text Solution
|
- Treatment of alkaline KMnO4 solution with KI solution oxidizes iodide ...
Text Solution
|
- If an extra electron is added to the hypothetical molecule C2 this ext...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following the square planar geometry is exhibited by:
Text Solution
|
- The correct pair of orbitals involved in t-bonding between metal and C...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic moment (in muB) of [Ni(dimethylglyxoimate)""2] complex is...
Text Solution
|
- A compound is formed by two elements M and N. Element N forms hexagona...
Text Solution
|
- If the velocity of the revolving electron of He^(+) in the first orbit...
Text Solution
|