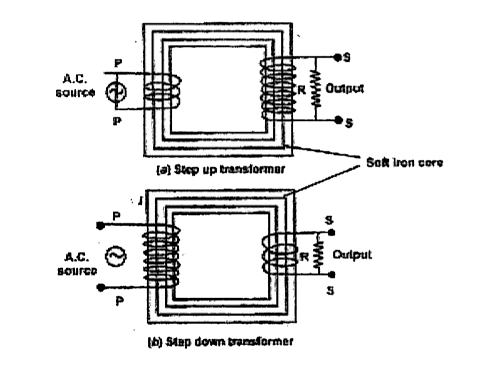
Transformer : It is an electrical device which can convert low alternating current at high voltage into high alternating current at low voltage and vice-versa.
Principle : Its working is based on the principle of mutual induction i.e., induced emf is produced in a coil whenever magnetic flux linked with the neighbouring coil changes.
Theory : Let `E_p` is alternating source of emf connected to primary coil and hence alternating current flows through the primary coil.
Due to the alternating current in the primary coil, a changing magnetic field and a changing magnetic flux gets linked with the coil.
This changing magnetic flux induces an alternating emf `(E_s)` in the secondary coil.
Let `N_p` = Number of turns in the primary coil.
`N_s` = Number of turns in the secondary coil.
If transformer is ideal, then whole of magnetic flux produced by the turns of primary coil gets coupled with (or linked with) the secondary coil.
`(d phi B)/(dt)=` Rate of change of magnetic flux in each turn of the coils.
`E_(p)= -N_(p)= (d phi B)/(dt)" ""..........."(i)`
`E_(s)= -N_(s)= (d phi B)/(dt)" ""..........."(ii)`
Divide eq. (ii) by eqn. (i)
`(E_s)/(E_p)= (N_s)/(N_p)`
Where `(N_s)/(N_p)= K =` Transformation ratio or turns ratio
So `(E_s)/(E_p)= (N_s)/(N_p)= K`
For step-down transformer, `K lt 1`
`implies N_(s) Lt N_(p)" and "E_(s) lt E_(p)`
Output alternating voltage is less than the input alternating voltage.
For step-up transformer : `K gt 1`
`implies N_(s) gt N_(p)" and "E_(s) gt E_(p)`
Output alternating voltage is greater than the input alternating voltage.
For an ideal transformer
Output power = Input power
`implies E_(s) I_(s)= E_(p) I_(p)`
`impies (E_s)/(E_p)= (I_p)/(I_s)`
`implies E propto (1)/(I)`
Whatever is gained in voltage ratio, is lost in the current ratio and vice-versa.
It is clear that for the same tranfer, voltage increases with the decrease in current and vice-versa.
Efficiency of a transformer `= eta= ("Output power")/("Input power")`
`eta= (E_(s)I_(s))/(E_(p)I_(p))`
For an ideal transformer, `eta` is 100%. But practically, there is no ideal transformer. Efficiency of transformer varies from 90-99%. It means there are always some losses in a transformer.