Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRICAL DEVICES
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS|3 VideosELECTRICAL DEVICES
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise (MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS 1 MARKS)|7 VideosELECTRICAL DEVICES
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise SHORT ANSWERS TYPE QUESTIONS (3/4 MARKS)|5 VideosELECTRIC FIELD
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS (MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS)|4 VideosELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION|Exercise Most Expected Questions|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
BETTER CHOICE PUBLICATION-ELECTRICAL DEVICES-LONG ANSWERS TYPE QUESTIONS (5/6 MARKS)
- What are copper loss, iron loss and hysteresis loss in transformer?
Text Solution
|
- What are copper loss, iron loss and hysteresis loss in transformer?
Text Solution
|
- What is the principle of a transformer ? Explain the theory and its ap...
Text Solution
|
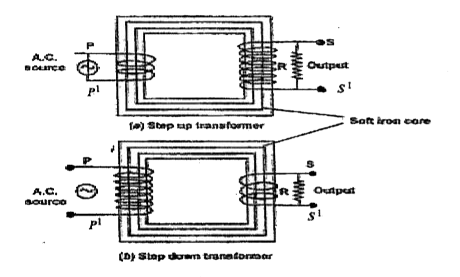
- With the help of labelled diagram, describe the principle,construction...
Text Solution
|
- Establish relation between voltage and current in primary and secondar...
Text Solution
|
- Give two reasons for power loss in a transformer.
Text Solution
|
- Give the principle, construction and working of an a.c. generator.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the construction , principle and working of a D.C. motor. Find...
Text Solution
|