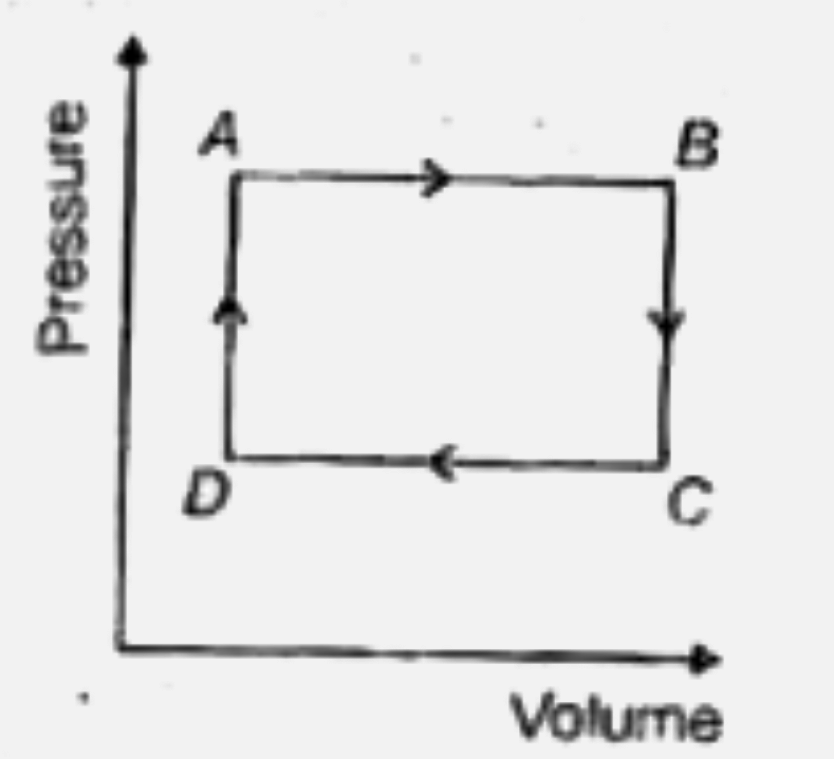
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RACE
ALLEN|Exercise Basic Maths (Dscillations) (Kinematics of SHM)|20 VideosRACE
ALLEN|Exercise Basic Maths (Oscillations) (Energy & spring pendulum)|17 VideosRACE
ALLEN|Exercise Basic Maths (Thermal Physics) (Kinetic theory of gasess)|12 VideosNEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION
ALLEN|Exercise EXERCISE-III|28 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ALLEN|Exercise Example|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ALLEN-RACE-Basic Maths (Thermal Physics) (Thermodynamic process)
- The pressure and volume of a gas are changed as shown in the p-V diagr...
Text Solution
|
- The efficiency of a Carnot's engine at a particular source and sink te...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal refrigerator runs between -23^@C and 27^@C. Find the heat rej...
Text Solution
|
- Selcet the incorrect relation. (Where symbols have their usual meaning...
Text Solution
|
- Select the incorrect statement about the specific heats of a gaseous s...
Text Solution
|
- Work done in the cyclic process shown in figure is
Text Solution
|
- Following figure shows P-T graph for four processes A, B, C and D.Sele...
Text Solution
|
- For polytropic process PV^(n) = constant, molar heat capacity (C(m)) o...
Text Solution
|
- For a certain process, pressure of diatomic gas varies according to th...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature inside and outside a refrigerator are 273K and 300K re...
Text Solution
|
- A box of negligible mass containing 2 moles of an ideal gas of molar ...
Text Solution
|
- Two ideal gases A & B are going through adiabatic process. Choose the ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of hydrogen, assumed to be ideal, is adiabatically expanded f...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process whose molar heat capacit...
Text Solution
|
- A gas expands such that its initial and final temperature are equal . ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic gas is carried along process ABCDEA as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monatomic gas at temperature T(0) ecpands slowly ...
Text Solution
|
- How many times a diatomic gas should be expanded adiabatically to redu...
Text Solution
|
- A diatomic ideal gas is heated at constant at constant volume until th...
Text Solution
|
- In a Carnot engine , when T2 = 0^@C and T1 = 200^@C , its efficiency i...
Text Solution
|