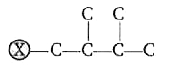A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MS CHOUHAN-HYDROCARBONS (ALKANES) -LEVEL - 2 (2. COMPREHENSION)
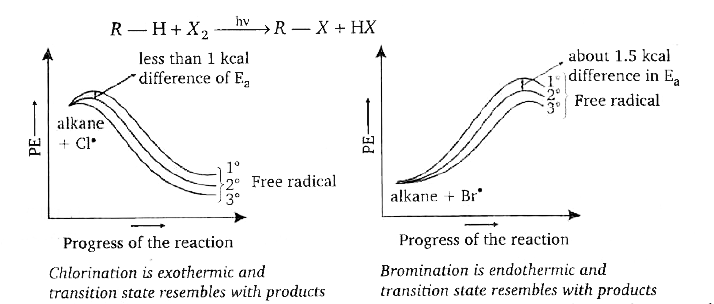
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|
- Halogenation is a substitution reaction, where halogen replaces one or...
Text Solution
|